1. a) You are required to develop a Hotel Management System in which the estimated lines of codes (LOC) is calculated to be 75000 and a review of the historical data reveals that the average productivity for this type of system is 244 LOC/PM and the labor rate is Rs 7,500 per month. What would be the estimated project cost and the estimated effort for this software package?
Ans:
1. b)What do you mean by reactive and proactive risk strategies?According to the risk table developed for a project, one of the risks is `staff turnover will be high'. List the possible steps to mitigate this risk.
Ans: Reactive: A response based risk management approach, which is dependent on accident evaluation and audit based findings.Reactive risk management solely depends on past accidental analysis and response.
Proactive: Adaptive, closed loop feedback control strategy based on measurement, observation of the present safety level and planned explicit target safety level with a creative intellectuality.Proactive risk management combines a mixed method of past, present and future prediction before finding solutions to avoid risks.
//2nd part to be added//
2. a)Define software quality assurance (SQA). Explain formal technical review with its importance in software development and list out the steps to conduct FTR
Ans:Software Quality Assurance (SQA) is simply a way to assure quality in the software. It is the set of activities which ensure processes, procedures as well as standards suitable for the project and implemented correctly.
Formal Technical Review (FTR) is a software quality control activity performed by software engineers.
//2nd part to be added//
2. b)What do you mean by SCM? Explain the importance of configuration audit and status reporting in SCM.
Ans:System Configuration Management (SCM) is an arrangement of exercises which controls change by recognizing the items for change, setting up connections between those things, making/characterizing instruments for overseeing diverse variants, controlling the changes being executed in the current framework, inspecting and revealing/reporting on the changes made.
//2nd part to be added//
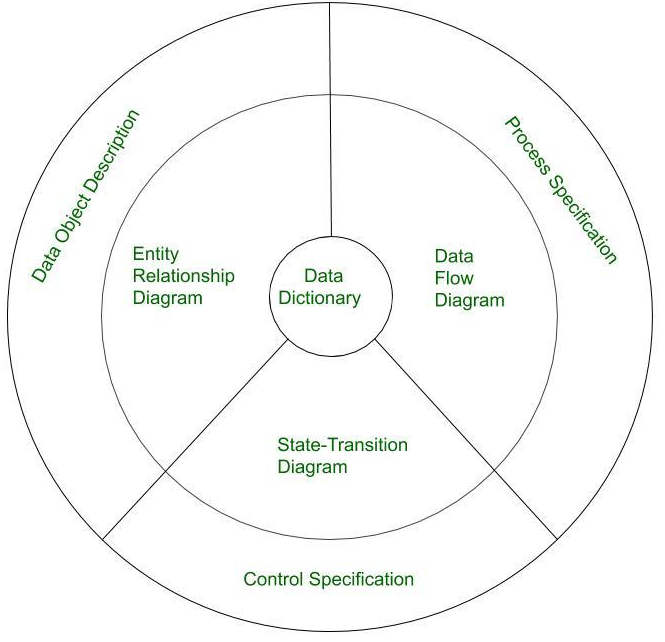
Ans:Analysis Model is a technical representation of the system. It acts as a link between system description and design model. In Analysis Modelling, information, behavior and functions of the system is defined and translated into the architecture, component and interface level design in the design modeling. Elements of Analysis Model:
-
Data Dictionary: It is a repository that consists of description of all data objects used or produced by software. It stores the collection of data present in the software. It is a very crucial element of the analysis model. It acts as a centralized repository and also helps in modelling of data objects defined during software requirements.
-
Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD): It depicts relationship between data objects and used in conducting of data modelling activity. The attributes of each object in the Entity Relationship Diagram can be described using Data object description. It provides the basis for activity related to data design.
-
Data Flow Diagram (DFD): It depicts the functions that transform data flow and it also shows how data is transformed when moving from input to output. It provides the additional information which is used during the analysis of information domain and serves as a basis for the modeling of function. It also enables the engineer to develop models of functional and information domain at the same time.
-
State Transition Diagram: It shows various modes of behavior (states) of the system and also shows the transitions from one state to other state in the system. It also provides the details of how system behaves due to the consequences of external events. It represents the behavior of a system by presenting its states and the events that cause the system to change state. It also describes what actions are taken due to the occurrence of a particular event.
-
Process Specification: It stores the description of each functions present in the data flow diagram. It describes the input to a function, the algorithm that is applied for transformation of input, and the output that is produced. It also shows regulations and barriers imposed on the performance characteristics that are applicable to the process, and layout constraints that could influence the way in which the process will be implemented.
-
Control Specification: It stores the additional information about the control aspects of the software. It is used to indicate how the software behaves when an event occurs and which processes are invoked due to the occurrence of the event. It also provides the details of the processes which are executed to manage events.
-
Data Object Description: It stores and provides the complete knowledge about a data object present and used in the software. It also gives us the details of attributes of the data object present in Entity Relationship Diagram. Hence, it incorporates all the data objects and its attributes.
3. b) What do you mean by design model? List any six design principles.Explain Data-flow architecture.
Ans: A design model in Software Engineering is an object-based picture or pictures that represent the use cases for a system. Or to put it another way, it is the means to describe a system's implementation and source code in a diagrammatic fashion.
//2nd part to be added//
4. a)Design a Level 1 DFD for a Food Ordering System. Include following requirements in your design.
- Customer can place an Order. The Order Food process receives the Order, forwards it to the Kitchen, store it in the Order data store, and store the updated Inventory details in the Inventory data store. The process also deliver a Bill to the Customer.
- Manager can receive Reports through the Generate Reports process, which takes Inventory details and Orders as input from the Inventory and Order data store respectively.
- Manager can also initiate the Order Inventory process by providing Inventory order. The process forwards the Inventory order to the Supplier and stores the updated Inventory details in the Inventory data store
Ans:
4. b) What do you mean by software testing? List out the objective of testing. Explain software testing strategies with examples.
Ans: Software testing is a process of identifying the correctness of software by considering its all attributes (Reliability, Scalability, Portability, Re-usability, Usability) and evaluating the execution of software components to find the software bugs or errors or defects.
The major objectives of Software testing are as follows:
- To evaluate the software performance,usability and reliability
- Finding defects which may get created by the programmer while developing the software.
- Gaining confidence in and providing information about the level of quality.
- To prevent defects.
- To ensure that it satisfies the Business Requirement Specification and System Requirement Specifications.
- To gain the confidence of the customers by providing them a quality product.
//3rd part to be added//
5. a)What are the importance of validation testing? Define cyclomatic complexity. Draw flow graph and find the cyclomatic complexity of the following code:
Int fun(int x, int y){
while(x!=y){
if(x>y)
x=x-y;
else
y=y-x;
}
return x;
}Ans:
5. b) What do you mean by Encapsulation? What are the steps involved in identifying the elements of an Object model?
Ans:
6. a) Differentiate between object oriented analysis and object oriented design.Explain the importance of domain analysis in OOAD.
Ans:
6. b) What do you mean by design patterns?Explain the importance of object oriented analysis and design in software development.
Ans:
A software process (also knows as software methodology) is a set of related activities that leads to the production of the software. These activities may involve the development of the software from the scratch, or, modifying an existing system.
Any software process must include the following four activities:
- Software specification (or requirements engineering): Define the main functionalities of the software and the constrains around them.
- Software design and implementation: The software is to be designed and programmed.
- Software verification and validation: The software must conforms to it’s specification and meets the customer needs.
- Software evolution (software maintenance): The software is being modified to meet customer and market requirements changes.
A software process model is an abstraction of the actual process, which is being described. It can also be defined as a simplified representation of a software process. Each model represents a process from a specific perspective. Basic software process models on which different type of software process models can be implemented:
-
A workflow Model: It is the sequential series of tasks and decisions that make up a business process.
-
The Waterfall Model: It is a sequential design process in which progress is seen as flowing steadily downwards. Phases in waterfall model: (i) Requirements Specification (ii) Software Design (iii) Implementation (iv) Testing
-
Dataflow Model: It is diagrammatic representation of the flow and exchange of information within a system. Evolutionary Development Model: Following activities are considered in this method: (i) Specification (ii) Development (iii) Validation
-
Role / Action Model: Roles of the people involved in the software process and the activities.
Software Quality Assurance (SQA) is simply a way to assure quality in the software. It is the set of activities which ensure processes, procedures as well as standards suitable for the project and implemented correctly.
Software Quality Assurance is a process which works parallel to development of a software. It focuses on improving the process of development of software so that problems can be prevented before they become a major issue. Software Quality Assurance is a kind of an Umbrella activity that is applied throughout the software process. Software Quality Assurance have:
- A quality management approach
- Formal technical reviews
- Multi testing strategy
- Effective software engineering technology
- Measurement and reporting mechanism
A function model or functional model is a structured representation of the functions (activities, actions, processes, operations) within the modeled system or subject area. A function model, similar with the activity model or process model, is a graphical representation of an enterprise's function within a defined scope. The purposes of the function model are to describe the functions and processes, assist with discovery of information needs, help identify opportunities, and establish a basis for determining product and service costs
Behavioral models identify and define the functions of the software being modeled. Behavioral models generally take three basic forms: state machines, control-flow models, and dataflow models. State machines provide a model of the software as a collection of defined states, events, and transitions. The software transitions from one state to the next by way of a guarded or unguarded triggering event that occurs in the modeled environment. Control-flow models depict how a sequence of events causes processes to be activated or deactivated. Data-flow behavior is typified as a sequence of steps where data moves through processes toward data stores or data sinks.