K510 nncase Developer's Guide
Document version: V1.0.1
Published: 2022-05-10
Disclaimer The products, services or features you purchase shall be subject to the commercial contracts and terms of Beijing Canaan Jiesi Information Technology Co., Ltd. ("the Company", the same hereinafter), and all or part of the products, services or features described in this document may not be within the scope of your purchase or use. Except as otherwise agreed in the contract, the Company disclaims all representations or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, reliability, completeness, marketing, specific purpose and non-aggression of any representations, information, or content of this document. Unless otherwise agreed, this document is provided as a guide for use only. Due to product version upgrades or other reasons, the contents of this document may be updated or modified from time to time without any notice.
Trademark Notices
""
Copyright ©2022 Beijing Canaan Jiesi Information Technology Co., Ltd This document is only applicable to the development and design of the K510 platform, without the written permission of the company, no unit or individual may disseminate part or all of the content of this document in any form.
Beijing Canaan Jiesi Information Technology Co., Ltd URL: canaan-creative.com Business Enquiries: salesAI@canaan-creative.com
# preface **Document purpose** This document is a description document for the use of the nncase/K510 compiler, providing users with how to install nncase, how to call the compiler APIs to compile neural network models, and runtime APIs to write AI inference programsReader Objects
The main people to whom this document (this guide) applies:
- Software developers
- Technical support personnel
Terms and acronyms
| term | Explanation/full name |
|---|---|
| PTQ | Post-training quantization, post-training quantization |
| MSE | mean-square error, mean squared error |
Revision history The revision history accumulates a description of each document update. The latest version of the document contains updates for all previous versions.
| The version number | Modified by | Date of revision | Revision Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| V1.0.1 | Publicity | 2022-05-10 | nncase_v1.6.1 |
| V1.0.0 | Zhang Yang/Zhang Jizhao/Yang Haoqi | 2022-05-06 | nncase_v1.6.0 |
| V0.9.0 | Publicity | 2022-04-01 | nncase_v1.5.0 |
| V0.8.0 | Zhang Yang/Zhang Jizhao | 2022-03-03 | nncase_v1.4.0 |
| V0.7.0 | Publicity | 2022-01-28 | nncase_v1.3.0 |
| V0.6.0 | Publicity | 2021-12-31 | nncase_v1.2.0 |
| V0.5.0 | Publicity | 2021-12-03 | nncase_v1.1.0 |
| V0.4.0 | Zhang Yang/Haoqi Yang/Zheng Qihang | 2021-10-29 | nncase_v1.0.0 |
| V0.3.0 | Zhang Yang / Yang Haoqi | 2021-09-28 | nncase_v1.0.0_rc1 |
| V0.2.0 | Zhang Yang / Yang Haoqi | 2021-09-02 | nncase_v1.0.0_beta2 |
| V0.1.0 | Zhang Yang / Yang Haoqi | 2021-08-31 | nncase_v1.0.0_beta1 |
[TOC]
- Ubuntu 18.04/20.04
The software environment requirements are shown in the following table:
| serial number | Software resources | illustrate |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Python | Python 3.6/3.7/3.8/3.9/3.10 |
| 2 | pip3 | pip3 version > = 20.3 |
| 3 | onnx | The onnx version is 1.9.0 |
| 4 | onnx-simplify | The onnx-simplifier version is 0.3.6 |
| 5 | onnxoptimizer | The onnxoptimizer version is 0.2.6 |
The hardware environment requirements are shown in the following table:
| serial number | Hardware resources | illustrate |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | K510 CRB | |
| 2 | SD card and card reader |
nncase is a neural network compiler designed for AI accelerators, and currently supports targets such as CPU/K210/K510
Features provided by nncase
- Support multiple input and multiple output networks, support multi-branch structure
- Static memory allocation, no heap memory required
- Operator merging and optimization
- Supports float and uint8/int8 quantization inference
- Supports post-training quantization, using floating-point models and quantization calibration sets
- Flat model with zero copy loading support
Neural network framework supported by nncase
- tflite
- onnx
- caffe
-
Simple end-to-end deployment
Reduce the number of interactions with users. Deployment on KPUs can be accomplished by using and deploying the same tools and processes for the CPU and GPU models. There is no need to set complex parameters, lower the threshold of use, and accelerate the iteration cycle of AI algorithms.
-
Make full use of the existing AI ecosystem
Attached to a framework widely used in the industry. On the one hand, it can improve its visibility and enjoy the dividends of a mature ecology. On the other hand, the development costs of small and medium-sized developers can be reduced, and the mature models and algorithms in the industry can be directly deployed.
-
Get the most out of your hardware
The advantage of NPU is that the performance is higher than that of CPU and GPU, and the DL Compiler must be able to fully utilize the performance of the hardware. Compiler also needs to adaptively optimize performance for the new model structure, so a new automatic optimization technique needs to be explored in addition to manual optimization.
-
Scalability and maintainability
Ability to support AI model deployments for K210, K510, and future chips. Some scalability needs to be provided at the architectural level. Adding a new Target is less expensive and allows you to reuse as many modules as possible. Accelerate the development of new products to achieve the technology accumulation of DL Compiler.
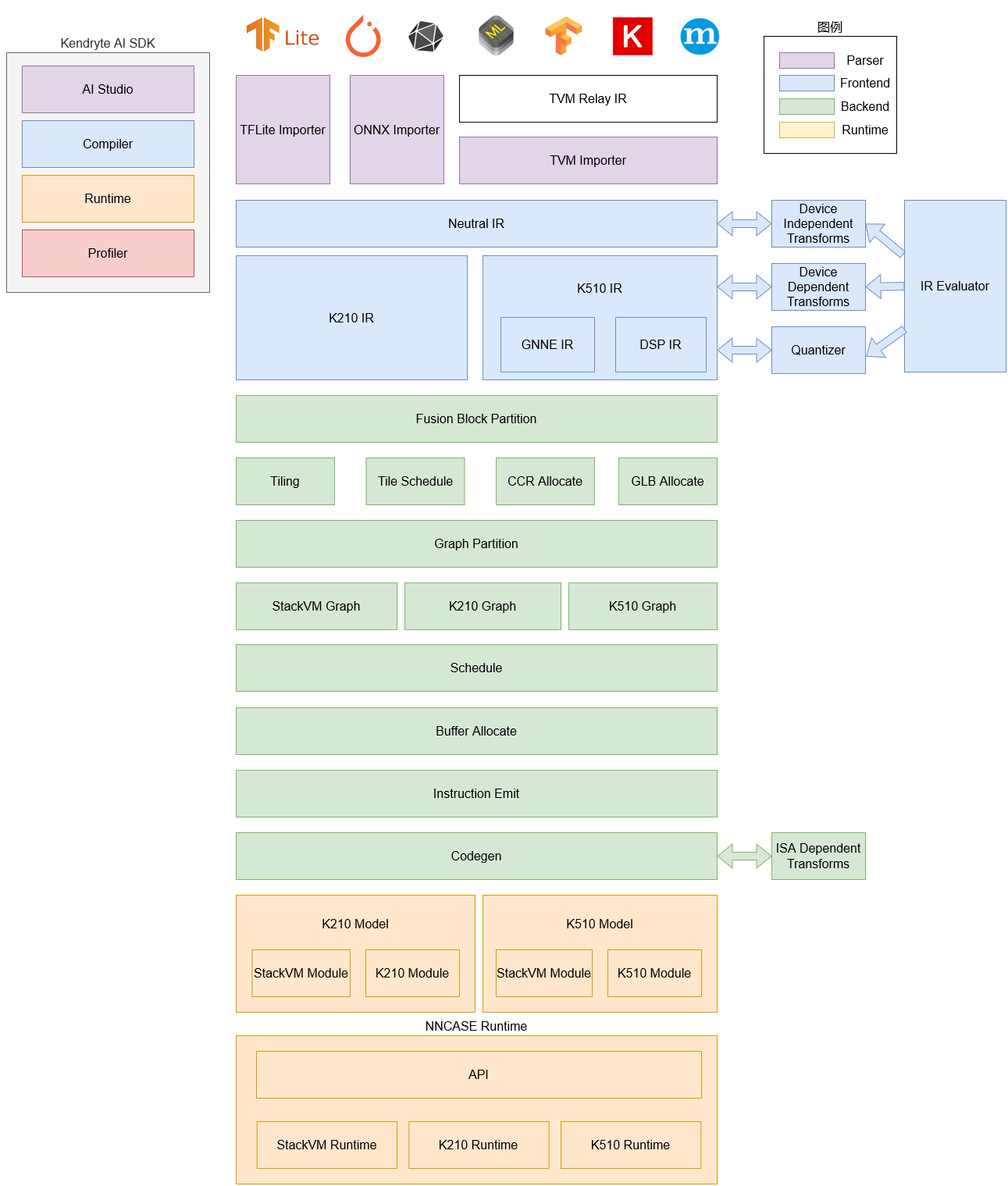
The nnncase software stack currently consists of two parts: compiler and runtime.
Compiler: Used to compile neural network models on a PC and eventually generate a kmodel file. It mainly includes importer, IR, Evaluator, Quantize, Transform optimization, Tiling, Partition, Schedule, Codegen and other modules.
- Importer: Imports models from other neural network frameworks into nncase
- IR: Middle representation, divided into importer-imported Neutral IR (device independent) and Nutral IR generated by lowering conversion Target IR (device dependent)
- Evaluator: Evaluator provides interpretive execution of IR and is often used in scenarios such as Constant Folding/PTQ Calibration
- Transform: For IR transformation and graph traversal optimization, etc
- Quantize: Quantize after training, add quantization markers to the tensor to be quantized, call Evaluator for interpretation execution according to the input correction set, collect tensor data range, insert quantization/dequantization nodes, and finally optimize to eliminate unnecessary quantization/dequantization nodes, etc
- Tiling: Limited by the lower memory capacity of the NPU, large chunks of computation need to be split. In addition, selecting the Tilling parameter when there is a large amount of data multiplexing in the calculation will have an impact on latency and bandwidth
- Partition: Divide the graph by ModuleType, each subgraph after splitting will correspond to RuntimeModule, different types of RuntimeModule correspond to different Devices (cpu/K510)
- Schedule: Generates a calculation order and allocates buffers based on the data dependencies in the optimized graph
- Codegen: Call the codegen corresponding to ModuleType for each subgraph to generate RuntimeModule
Runtime: Integrated into the user app, it provides functions such as loading kmodel/ setting input data, KPU execution, and obtaining output data
The compiler part of the nncase toolchain includes nncase and K510 compiler, both of which need to install the corresponding wheel package.
- The nncase wheel package wasreleased on nncase github, supporting Python 3.6/3.7/3.8/3.9/3.10, users can choose the corresponding version to download according to the operating system and Python
- The K510 compiler wheel package is in the x86_64 directory of the nncase SDK, does not depend on the Python version, and can be installed directly
If you do not have an Ubuntu environment, you can usenncase docker(Ubuntu 20.04 + Python 3.8).
cd /path/to/nncase_sdk
docker pull registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/kendryte/nncase:latest
docker run -it --rm -v `pwd`:/mnt -w /mnt registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/kendryte/nncase:latest /bin/bash -c "/bin/bash"The following takes Ubuntu 20.04 + Python 3.8 installation of nncase as an example
wget -P x86_64 https://github.com/kendryte/nncase/releases/download/v1.6.0/nncase-1.6.0.20220505-cp38-cp38-manylinux_2_24_x86_64.whl
pip3 install x86_64/*.whlnncase providesPython APIfor compiling/inferring deep learning models on a PC
| Operator | Is Supported |
|---|---|
| ABS | ✅ |
| ADD | ✅ |
| ARG_MAX | ✅ |
| ARG_MIN | ✅ |
| AVERAGE_POOL_2D | ✅ |
| BATCH_MATMUL | ✅ |
| CAST | ✅ |
| CEIL | ✅ |
| CONCATENATION | ✅ |
| CONV_2D | ✅ |
| BODY | ✅ |
| CUSTOM | ✅ |
| DEPTHWISE_CONV_2D | ✅ |
| DIV | ✅ |
| EQUAL | ✅ |
| EXP | ✅ |
| EXPAND_DIMS | ✅ |
| FLOOR | ✅ |
| FLOOR_DIV | ✅ |
| FLOOR_MOD | ✅ |
| FULLY_CONNECTED | ✅ |
| GREATER | ✅ |
| GREATER_EQUAL | ✅ |
| L2_NORMALIZATION | ✅ |
| LEAKY_RELU | ✅ |
| LESS | ✅ |
| LESS_EQUAL | ✅ |
| LOG | ✅ |
| LOGISTIC | ✅ |
| MAX_POOL_2D | ✅ |
| MAXIMUM | ✅ |
| MEAN | ✅ |
| MINIMUM | ✅ |
| I | ✅ |
| NEG | ✅ |
| NOT_EQUAL | ✅ |
| PAD | ✅ |
| PADV2 | ✅ |
| MIRROR_PAD | ✅ |
| PACK | ✅ |
| POW | ✅ |
| REDUCE_MAX | ✅ |
| REDUCE_MIN | ✅ |
| REDUCE_PROD | ✅ |
| RELU | ✅ |
| PRELU | ✅ |
| RELU6 | ✅ |
| RESHAPE | ✅ |
| RESIZE_BILINEAR | ✅ |
| RESIZE_NEAREST_NEIGHBOR | ✅ |
| ROUND | ✅ |
| RSQRT | ✅ |
| SHAPE | ✅ |
| WITHOUT | ✅ |
| SLICE | ✅ |
| SOFTMAX | ✅ |
| SPACE_TO_BATCH_ND | ✅ |
| SQUEEZE | ✅ |
| BATCH_TO_SPACE_ND | ✅ |
| STRIDED_SLICE | ✅ |
| SQRT | ✅ |
| SQUARE | ✅ |
| SUB | ✅ |
| SUM | ✅ |
| FISHY | ✅ |
| TILE | ✅ |
| TRANSPOSE | ✅ |
| TRANSPOSE_CONV | ✅ |
| QUANTIZE | ✅ |
| FAKE_QUANT | ✅ |
| DEQUANTIZE | ✅ |
| GATHER | ✅ |
| GATHER_ND | ✅ |
| ONE_HOT | ✅ |
| SQUARED_DIFFERENCE | ✅ |
| LOG_SOFTMAX | ✅ |
| SPLIT | ✅ |
| HARD_SWISH | ✅ |
| Operator | Is Supported |
|---|---|
| Abs | ✅ |
| Acos | ✅ |
| Acosh | ✅ |
| And | ✅ |
| ArgMax | ✅ |
| ArgMin | ✅ |
| Salty | ✅ |
| Asinh | ✅ |
| Add | ✅ |
| AveragePool | ✅ |
| BatchNormalization | ✅ |
| Cast | ✅ |
| Ceil | ✅ |
| To | ✅ |
| Clip | ✅ |
| Concat | ✅ |
| Constant | ✅ |
| ConstantOfShape | ✅ |
| Conv | ✅ |
| ConvTranspose | ✅ |
| Body | ✅ |
| Cosh | ✅ |
| CumSum | ✅ |
| DepthToSpace | ✅ |
| DequantizeLinear | ✅ |
| Div | ✅ |
| Dropout | ✅ |
| Life | ✅ |
| Exp | ✅ |
| Expand | ✅ |
| Equal | ✅ |
| Flatten | ✅ |
| Floor | ✅ |
| Gather | ✅ |
| GatherND | ✅ |
| Gemm | ✅ |
| GlobalAveragePool | ✅ |
| GlobalMaxPool | ✅ |
| Greater | ✅ |
| GreaterOrEqual | ✅ |
| Hardmax | ✅ |
| HardSigmoid | ✅ |
| HardSwish | ✅ |
| Identity | ✅ |
| InstanceNormalization | ✅ |
| LpNormalization | ✅ |
| LeakyRelu | ✅ |
| Less | ✅ |
| LessOrEqual | ✅ |
| Log | ✅ |
| LogSoftmax | ✅ |
| LRN | ✅ |
| LSTM | ✅ |
| MatMul | ✅ |
| MaxPool | ✅ |
| Max | ✅ |
| Min | ✅ |
| I | ✅ |
| Neg | ✅ |
| Not | ✅ |
| OneHot | ✅ |
| Pad | ✅ |
| Pow | ✅ |
| PRelu | ✅ |
| QuantizeLinear | ✅ |
| RandomNormal | ✅ |
| RandomNormalLike | ✅ |
| RandomUniform | ✅ |
| RandomUniformLike | ✅ |
| ReduceL1 | ✅ |
| ReduceL2 | ✅ |
| ReduceLogSum | ✅ |
| ReduceLogSumExp | ✅ |
| ReduceMax | ✅ |
| ReduceMean | ✅ |
| ReduceMin | ✅ |
| ReduceProd | ✅ |
| ReduceSum | ✅ |
| ReduceSumSquare | ✅ |
| Relu | ✅ |
| Reshape | ✅ |
| Resize | ✅ |
| ReverseSequence | ✅ |
| RoiAlign | ✅ |
| Round | ✅ |
| Village | ✅ |
| Shape | ✅ |
| Sign | ✅ |
| Without | ✅ |
| Birth | ✅ |
| Sigmoid | ✅ |
| Size | ✅ |
| Slice | ✅ |
| Softmax | ✅ |
| Softplus | ✅ |
| Softsign | ✅ |
| SpaceToDepth | ✅ |
| Split | ✅ |
| Sqrt | ✅ |
| Squeeze | ✅ |
| Sub | ✅ |
| Sum | ✅ |
| Fishy | ✅ |
| Tile | ✅ |
| TopK | ✅ |
| Transpose | ✅ |
| Trilu | ✅ |
| Upsample | ✅ |
| Unsqueeze | ✅ |
| Where | ✅ |
| Operator | Is Supported |
|---|---|
| Input | ✅ |
| Concat | ✅ |
| Convolution | ✅ |
| Eltwise | ✅ |
| Trade-ins | ✅ |
| relu | ✅ |
| Reshape | ✅ |
| Slice | ✅ |
| Softmax | ✅ |
| Split | ✅ |
| ContinuationIndicator | ✅ |
| Pooling | ✅ |
| BatchNorm | ✅ |
| Scale | ✅ |
| Reverse | ✅ |
| LSTM | ✅ |
| InnerProduct | ✅ |
At present, the compilation model API supports deep learning frameworks such as tflite/onnx/caffe.
Feature description
CompileOptions class for configuring nncase compilation options
Class definition
py::class_<compile_options>(m, "CompileOptions")
.def(py::init())
.def_readwrite("target", &compile_options::target)
.def_readwrite("quant_type", &compile_options::quant_type)
.def_readwrite("w_quant_type", &compile_options::w_quant_type)
.def_readwrite("use_mse_quant_w", &compile_options::use_mse_quant_w)
.def_readwrite("split_w_to_act", &compile_options::split_w_to_act)
.def_readwrite("preprocess", &compile_options::preprocess)
.def_readwrite("swapRB", &compile_options::swapRB)
.def_readwrite("mean", &compile_options::mean)
.def_readwrite("std", &compile_options::std)
.def_readwrite("input_range", &compile_options::input_range)
.def_readwrite("output_range", &compile_options::output_range)
.def_readwrite("input_shape", &compile_options::input_shape)
.def_readwrite("letterbox_value", &compile_options::letterbox_value)
.def_readwrite("input_type", &compile_options::input_type)
.def_readwrite("output_type", &compile_options::output_type)
.def_readwrite("input_layout", &compile_options::input_layout)
.def_readwrite("output_layout", &compile_options::output_layout)
.def_readwrite("model_layout", &compile_options::model_layout)
.def_readwrite("is_fpga", &compile_options::is_fpga)
.def_readwrite("dump_ir", &compile_options::dump_ir)
.def_readwrite("dump_asm", &compile_options::dump_asm)
.def_readwrite("dump_quant_error", &compile_options::dump_quant_error)
.def_readwrite("dump_dir", &compile_options::dump_dir)
.def_readwrite("benchmark_only", &compile_options::benchmark_only);Each property is described below
| Property name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| target | string | be | Specify the compilation target, such as 'k210', 'k510' |
| quant_type | string | not | Specify the data quantization type, such as 'uint8', 'int8' |
| w_quant_type | string | not | Specify the weight quantization type, such as 'uint8', 'int8', default to 'uint8' |
| use_mse_quant_w | bool | not | Specifies whether to use the mean-square error (MSE) algorithm to optimize the quantization parameters when quantizing weights |
| split_w_to_act | bool | not | Specifies whether to balance partial weight data into active data |
| preprocess | bool | not | Whether pre-processing is enabled or not, the default is False |
| swapRB | bool | not | Whether to exchange RGB input data between the red and blue channels (RGB--> BGR or BGR->RGB), the default is False |
| mean | list | not | Preprocessing normalizes the parameter mean, which defaults to[0, 0, 0] |
| Std | list | not | Preprocessing normalizes the parameter variance, which defaults to [1, 1, 1] |
| input_range | list | not | The range of floating-point numbers after dequantization of the input data, which defaults to[0, 1] |
| output_range | list | not | The range of floating-point numbers before the fixed-point data is output, which defaults to blank |
| input_shape | list | not | Specify the shape of the input data, the layout of the input_shape needs to be consistent with the input layout, and the input_shape of the input data is inconsistent with the input shape of the model, and the bitbox operation (resize/pad, etc.) will be performed. |
| letterbox_value | float | not | Specifies the padding value of the pre-processing fetchbox |
| input_type | string | not | Specifies the type of input data, defaulting to 'float32' |
| output_type | string | not | Specifies the type of output data, such as 'float32', 'uint8' (only for specified quantization), defaults to 'float32' |
| input_layout | string | not | Specify the layout of the input data, such as 'NCHW', 'NHWC'. If the input data layout is different from the model itself, nncase inserts transpose for conversion |
| output_layout | string | not | Specify the output data for the layout, such as 'NCHW', 'NHWC'. If the output data layout is different from the model itself, nncase will insert transpose for conversion |
| model_layout | string | not | Specify the layout of the model, which defaults to blank, and specifies when the tflite model layout is 'NCHW' and the Onnx and Caffe models are 'NHWC' |
| is_fpga | bool | not | Specifies whether kmodel is used for FPGAs, which defaults to False |
| dump_ir | bool | not | Specifies whether dump IR, defaults to False |
| dump_asm | bool | not | Specifies whether the dump asm assembly file, which defaults to False |
| dump_quant_error | bool | not | Specifies whether dump quantizes the model error before and after |
| dump_dir | string | not | After specifying the dump_ir and other switches earlier, here you specify the directory of dump, which defaults to an empty string |
| benchmark_only | bool | not | Specifies whether kmodel is used only for benchmark, which defaults to False |
- Input range is the range of floating-point numbers, that is, if the input data type is uint8, then the input range is the range after dequantization to floating point (can not be 0 ~ 1), which can be freely specified.
- input_shape need to be specified according to the input_layout, [1,224,224,3]for example, if the input_layout is NCHW, the input_shape needs to be specified as[1,3,224,224]; input_layout is NHWC, the input_shape needs to be specified as[1,224,224,3];
- mean and std are parameters for normalize floating-point numbers, which the user is free to specify;
- When using the letterbox function, you need to limit the input size to 1.5MB, and the size of a single channel is within 0.75MB;
For example:
- The input data type is set to uint8, input_range set to[0,255], the role of dequantization is only to convert the type, convert the data of uint8 to float32, and the mean and std parameters can still be specified according to the data of 0~255
- The input data type is set to uint8, input_range set [0,1]to, the fixed-point number is dequantized to a [0,1]floating-point number in the range, and mean and std need to be specified according to the new floating-point number range.
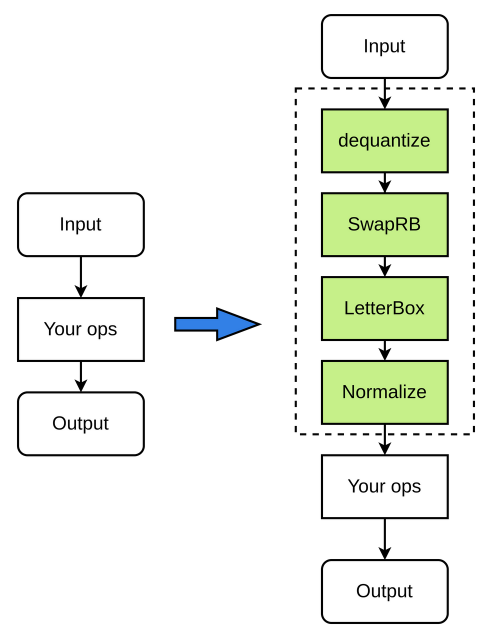
The pre-processing process is as follows (the green nodes in the figure are optional):
Code example
Instantiate CompileOptions, configure the values of each property
# compile_options
compile_options = nncase.CompileOptions()
compile_options.target = target
compile_options.input_type = 'float32' # or 'uint8' 'int8'
compile_options.output_type = 'float32' # or 'uint8' 'int8'. Only work in PTQ
compile_options.output_range = [] # Only work in PTQ and output type is not "float32"
compile_options.preprocess = True # if False, the args below will unworked
compile_options.swapRB = True
compile_options.input_shape = [1,224,224,3] # keep layout same as input layout
compile_options.input_layout = 'NHWC'
compile_options.output_layout = 'NHWC'
compile_options.model_layout = '' # Specific it when tflite model with "NCHW" layout and Onnx(Caffe) model with "NHWC" layout
compile_options.mean = [0,0,0]
compile_options.std = [1,1,1]
compile_options.input_range = [0,1]
compile_options.letterbox_value = 114. # pad what you want
compile_options.dump_ir = True
compile_options.dump_asm = True
compile_options.dump_dir = 'tmp'Feature description
ImportOptions class for configuring nncase import options
Class definition
py::class_<import_options>(m, "ImportOptions")
.def(py::init())
.def_readwrite("output_arrays", &import_options::output_arrays);Each property is described below
| Property name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| output_arrays | string | not | Output name |
Code example
Instantiate ImageOptions, configure the values of each property
# import_options
import_options = nncase.ImportOptions()
import_options.output_arrays = 'output' # Your output node nameFeature description
PTQTensorOptions class for configuring nncase PTQ options
Class definition
py::class_<ptq_tensor_options>(m, "PTQTensorOptions")
.def(py::init())
.def_readwrite("calibrate_method", &ptq_tensor_options::calibrate_method)
.def_readwrite("samples_count", &ptq_tensor_options::samples_count)
.def("set_tensor_data", [](ptq_tensor_options &o, py::bytes bytes) {
uint8_t *buffer;
py::ssize_t length;
if (PyBytes_AsStringAndSize(bytes.ptr(), reinterpret_cast<char **>(&buffer), &length))
throw std::invalid_argument("Invalid bytes");
o.tensor_data.assign(buffer, buffer + length);
});Each property is described below
| The field name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| calibrate_method | string | not | Calibration method , supports 'no_clip', 'l2', 'kld_m0', 'kld_m1', 'kld_m2', 'cdf', default is 'no_clip' |
| samples_count | int | not | The number of samples |
Feature description
Set the correction data
Interface definition
set_tensor_data(calib_data)Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| calib_data | byte[] | be | Correct the data |
The return value
N/A
Code example
# ptq_options
ptq_options = nncase.PTQTensorOptions()
ptq_options.samples_count = cfg.generate_calibs.batch_size
ptq_options.set_tensor_data(np.asarray([sample['data'] for sample in self.calibs]).tobytes())Feature description
Compiler class for compiling neural network models
Class definition
py::class_<compiler>(m, "Compiler")
.def(py::init(&compiler::create))
.def("import_tflite", &compiler::import_tflite)
.def("import_onnx", &compiler::import_onnx)
.def("import_caffe", &compiler::import_caffe)
.def("compile", &compiler::compile)
.def("use_ptq", py::overload_cast<ptq_tensor_options>(&compiler::use_ptq))
.def("gencode", [](compiler &c, std::ostream &stream) { c.gencode(stream); })
.def("gencode_tobytes", [](compiler &c) {
std::stringstream ss;
c.gencode(ss);
return py::bytes(ss.str());
})
.def("create_evaluator", [](compiler &c, uint32_t stage) {
auto &graph = c.graph(stage);
return std::make_unique<graph_evaluator>(c.target(), graph);
});Code example
compiler = nncase.Compiler(compile_options)Feature description
Import the tflite model
Interface definition
import_tflite(model_content, import_options)Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| model_content | byte[] | be | Read the model content |
| import_options | ImportOptions | be | Import options |
The return value
N/A
Code example
model_content = read_model_file(model)
compiler.import_tflite(model_content, import_options)Feature description
Import the onnx model
Interface definition
import_onnx(model_content, import_options)Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| model_content | byte[] | be | Read the model content |
| import_options | ImportOptions | be | Import options |
The return value
N/A
Code example
model_content = read_model_file(model)
compiler.import_onnx(model_content, import_options)Feature description
Import the caffe model
Users need to compile/install caffe on the local machine.
Interface definition
import_caffe(caffemodel, prototxt)Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| caffemodel | byte[] | be | Read the caffemodel content |
| prototxt | byte[] | be | Read the prototxt content |
The return value
N/A
Code example
# import
caffemodel = read_model_file('test.caffemodel')
prototxt = read_model_file('test.prototxt')
compiler.import_caffe(caffemodel, prototxt)Feature description
Set PTQ configuration options
Interface definition
use_ptq(ptq_options)Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ptq_options | PTQTensorOptions | be | PTQ configuration options |
The return value
N/A
Code example
compiler.use_ptq(ptq_options)Feature description
Compile the neural network model
Interface definition
compile()Input parameters
N/A
The return value
N/A
Code example
compiler.compile()Feature description
Generates a stream of code bytes
Interface definition
gencode_tobytes()Input parameters
N/A
The return value
bytes[]
Code example
kmodel = compiler.gencode_tobytes()
with open(os.path.join(infer_dir, 'test.kmodel'), 'wb') as f:
f.write(kmodel)The following example uses the model and python compilation script
- The model is located in the /path/to/nncase_sdk/examples/models/subdirectory
- The python compilation script is located in the /path/to/nncase_sdk/examples/scripts subdirectory
- Mobilenetv2_tflite_fp32_image.py script is as follows
import nncase
import os
import argparse
def read_model_file(model_file):
with open(model_file, 'rb') as f:
model_content = f.read()
return model_content
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(prog="nncase")
parser.add_argument("--target", type=str, help='target to run')
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, help='model file')
args = parser.parse_args()
# compile_options
dump_dir = 'tmp/mobilenetv2_tflite_fp32_image'
compile_options = nncase.CompileOptions()
compile_options.target = args.target
compile_options.dump_ir = True
compile_options.dump_asm = True
compile_options.dump_dir = dump_dir
# compiler
compiler = nncase.Compiler(compile_options)
# import_options
import_options = nncase.ImportOptions()
# import
model_content = read_model_file(args.model)
compiler.import_tflite(model_content, import_options)
# compile
compiler.compile()
# kmodel
kmodel = compiler.gencode_tobytes()
with open(os.path.join(dump_dir, 'test.kmodel'), 'wb') as f:
f.write(kmodel)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()- Run the following command to compile the tflite model of mobiletv2, target k510
cd /path/to/nncase_sdk/examples
python3 scripts/mobilenetv2_tflite_fp32_image.py --target k510 --model models/mobilenet_v2_1.0_224.tflite- For onnx models, it is recommended to simplify usingONNX Simplifierbefore compiling with nncase
- mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image.py script is as follows
import os
import onnxsim
import onnx
import nncase
import argparse
def parse_model_input_output(model_file):
onnx_model = onnx.load(model_file)
input_all = [node.name for node in onnx_model.graph.input]
input_initializer = [node.name for node in onnx_model.graph.initializer]
input_names = list(set(input_all) - set(input_initializer))
input_tensors = [node for node in onnx_model.graph.input if node.name in input_names]
# input
inputs= []
for _, e in enumerate(input_tensors):
onnx_type = e.type.tensor_type
input_dict = {}
input_dict['name'] = e.name
input_dict['dtype'] = onnx.mapping.TENSOR_TYPE_TO_NP_TYPE[onnx_type.elem_type]
input_dict['shape'] = [(i.dim_value if i.dim_value != 0 else d) for i, d in zip(
onnx_type.shape.dim, [1, 3, 224, 224])]
inputs.append(input_dict)
return onnx_model, inputs
def onnx_simplify(model_file, dump_dir):
onnx_model, inputs = parse_model_input_output(model_file)
onnx_model = onnx.shape_inference.infer_shapes(onnx_model)
input_shapes = {}
for input in inputs:
input_shapes[input['name']] = input['shape']
onnx_model, check = onnxsim.simplify(onnx_model, input_shapes=input_shapes)
assert check, "Simplified ONNX model could not be validated"
model_file = os.path.join(dump_dir, 'simplified.onnx')
onnx.save_model(onnx_model, model_file)
return model_file
def read_model_file(model_file):
with open(model_file, 'rb') as f:
model_content = f.read()
return model_content
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(prog="nncase")
parser.add_argument("--target", type=str, help='target to run')
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, help='model file')
args = parser.parse_args()
dump_dir = 'tmp/mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image'
if not os.path.exists(dump_dir):
os.makedirs(dump_dir)
# onnx simplify
model_file = onnx_simplify(args.model, dump_dir)
# compile_options
compile_options = nncase.CompileOptions()
compile_options.target = args.target
compile_options.dump_ir = True
compile_options.dump_asm = True
compile_options.dump_dir = dump_dir
# compiler
compiler = nncase.Compiler(compile_options)
# import_options
import_options = nncase.ImportOptions()
# import
model_content = read_model_file(model_file)
compiler.import_onnx(model_content, import_options)
# compile
compiler.compile()
# kmodel
kmodel = compiler.gencode_tobytes()
with open(os.path.join(dump_dir, 'test.kmodel'), 'wb') as f:
f.write(kmodel)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()- Run the following command to compile the onnx model of mobiletv2, target k510
cd /path/to/nncase_sdk/examples
python3 scripts/mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image.py --target k510 --model models/mobilenetv2-7.onnx- The caffe wheel package istaken fromkendryte caffe
- conv2d_caffe_fp32.py script is as follows
import nncase
import os
import argparse
def read_model_file(model_file):
with open(model_file, 'rb') as f:
model_content = f.read()
return model_content
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(prog="nncase")
parser.add_argument("--target", type=str, help='target to run')
parser.add_argument("--caffemodel", type=str, help='caffemodel file')
parser.add_argument("--prototxt", type=str, help='prototxt file')
args = parser.parse_args()
# compile_options
dump_dir = 'tmp/conv2d_caffe_fp32'
compile_options = nncase.CompileOptions()
compile_options.target = args.target
compile_options.dump_ir = True
compile_options.dump_asm = True
compile_options.dump_dir = dump_dir
# compiler
compiler = nncase.Compiler(compile_options)
# import_options
import_options = nncase.ImportOptions()
# import
caffemodel = read_model_file(args.caffemodel)
prototxt = read_model_file(args.prototxt)
compiler.import_caffe(caffemodel, prototxt)
# compile
compiler.compile()
# kmodel
kmodel = compiler.gencode_tobytes()
with open(os.path.join(dump_dir, 'test.kmodel'), 'wb') as f:
f.write(kmodel)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()- Run the following command to compile the caffe model of conv2d, with the target k510
cd /path/to/nncase_sdk/examples
python3 scripts/conv2d_caffe_fp32.py --target k510 --caffemodel models/test.caffemodel --prototxt models/test.prototxt- For onnx models, it is recommended to simplify usingONNX Simplifierbefore compiling with nncase
- Mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_preprocess.py script is as follows
import os
import onnxsim
import onnx
import nncase
import argparse
def parse_model_input_output(model_file):
onnx_model = onnx.load(model_file)
input_all = [node.name for node in onnx_model.graph.input]
input_initializer = [node.name for node in onnx_model.graph.initializer]
input_names = list(set(input_all) - set(input_initializer))
input_tensors = [node for node in onnx_model.graph.input if node.name in input_names]
# input
inputs= []
for _, e in enumerate(input_tensors):
onnx_type = e.type.tensor_type
input_dict = {}
input_dict['name'] = e.name
input_dict['dtype'] = onnx.mapping.TENSOR_TYPE_TO_NP_TYPE[onnx_type.elem_type]
input_dict['shape'] = [(i.dim_value if i.dim_value != 0 else d) for i, d in zip(
onnx_type.shape.dim, [1, 3, 224, 224])]
inputs.append(input_dict)
return onnx_model, inputs
def onnx_simplify(model_file, dump_dir):
onnx_model, inputs = parse_model_input_output(model_file)
onnx_model = onnx.shape_inference.infer_shapes(onnx_model)
input_shapes = {}
for input in inputs:
input_shapes[input['name']] = input['shape']
onnx_model, check = onnxsim.simplify(onnx_model, input_shapes=input_shapes)
assert check, "Simplified ONNX model could not be validated"
model_file = os.path.join(dump_dir, 'simplified.onnx')
onnx.save_model(onnx_model, model_file)
return model_file
def read_model_file(model_file):
with open(model_file, 'rb') as f:
model_content = f.read()
return model_content
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(prog="nncase")
parser.add_argument("--target", type=str, help='target to run')
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, help='model file')
args = parser.parse_args()
dump_dir = 'tmp/mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_preprocess'
if not os.path.exists(dump_dir):
os.makedirs(dump_dir)
# onnx simplify
model_file = onnx_simplify(args.model, dump_dir)
# compile_options
compile_options = nncase.CompileOptions()
compile_options.target = args.target
compile_options.input_type = 'uint8'
compile_options.preprocess = True
compile_options.swapRB = True
compile_options.input_layout = 'NHWC'
compile_options.output_layout = 'NCHW'
compile_options.input_shape = [1, 256, 256, 3]
compile_options.mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
compile_options.std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
compile_options.input_range = [0, 1]
compile_options.dump_ir = True
compile_options.dump_asm = True
compile_options.dump_dir = dump_dir
# compiler
compiler = nncase.Compiler(compile_options)
# import_options
import_options = nncase.ImportOptions()
# import
model_content = read_model_file(model_file)
compiler.import_onnx(model_content, import_options)
# compile
compiler.compile()
# kmodel
kmodel = compiler.gencode_tobytes()
with open(os.path.join(dump_dir, 'test.kmodel'), 'wb') as f:
f.write(kmodel)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()- Run the following command to compile the onnx model of mobiletv2 with the target k510
cd /path/to/nncase_sdk/examples
python3 scripts/mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_preprocess.py --target k510 --model models/mobilenetv2-7.onnx- Mobilenetv2_tflite_uint8_image.py script is as follows
import nncase
import os
import argparse
import numpy as np
def read_model_file(model_file):
with open(model_file, 'rb') as f:
model_content = f.read()
return model_content
def generate_data(shape, batch):
shape[0] *= batch
data = np.random.rand(*shape).astype(np.float32)
return data
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(prog="nncase")
parser.add_argument("--target", type=str, help='target to run')
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, help='model file')
args = parser.parse_args()
input_shape = [1, 224, 224, 3]
# compile_options
dump_dir = 'tmp/mobilenetv2_tflite_uint8_image'
compile_options = nncase.CompileOptions()
compile_options.target = args.target
compile_options.input_type = 'float32'
compile_options.input_layout = 'NHWC'
compile_options.output_layout = 'NHWC'
compile_options.dump_ir = True
compile_options.dump_asm = True
compile_options.dump_dir = dump_dir
# compiler
compiler = nncase.Compiler(compile_options)
# import_options
import_options = nncase.ImportOptions()
# quantize model
compile_options.quant_type = 'uint8'
# ptq_options
ptq_options = nncase.PTQTensorOptions()
ptq_options.samples_count = 10
ptq_options.set_tensor_data(generate_data(input_shape, ptq_options.samples_count).tobytes())
# import
model_content = read_model_file(args.model)
compiler.import_tflite(model_content, import_options)
# compile
compiler.use_ptq(ptq_options)
compiler.compile()
# kmodel
kmodel = compiler.gencode_tobytes()
with open(os.path.join(dump_dir, 'test.kmodel'), 'wb') as f:
f.write(kmodel)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()- Run the following command to compile the tflite model of uint8 quantized mobiletv2, target k510
cd /path/to/nncase_sdk/examples
python3 scripts/mobilenetv2_tflite_uint8_image.py --target k510 --model models/mobilenet_v2_1.0_224.tfliteIn addition to the APs of the compiled model, nncase also provides the APIs of the inference model, which can be inferred on the PC before the compilation of the kmodel, which is used to verify whether the nncase inference results and the runtime results of the corresponding deep learning framework are consistent.
Feature description
The MemoryRange class, which is used to represent a range of memory
Class definition
py::class_<memory_range>(m, "MemoryRange")
.def_readwrite("location", &memory_range::memory_location)
.def_property(
"dtype", [](const memory_range &range) { return to_dtype(range.datatype); },
[](memory_range &range, py::object dtype) { range.datatype = from_dtype(py::dtype::from_args(dtype)); })
.def_readwrite("start", &memory_range::start)
.def_readwrite("size", &memory_range::size);Each property is described below
| Property name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| location | int | not | Memory position, 0 for input, 1 for output, 2 for rdata, 3 for data, 4 for shared_data |
| dtype | Python data type | not | data type |
| start | int | not | Memory start address |
| size | int | not | Memory size |
Code example
Instantiate MemoryRange
mr = nncase.MemoryRange()Feature description
The RuntimeTensor class, which represents the runtime tensor
Class definition
py::class_<runtime_tensor>(m, "RuntimeTensor")
.def_static("from_numpy", [](py::array arr) {
auto src_buffer = arr.request();
auto datatype = from_dtype(arr.dtype());
auto tensor = host_runtime_tensor::create(
datatype,
to_rt_shape(src_buffer.shape),
to_rt_strides(src_buffer.itemsize, src_buffer.strides),
gsl::make_span(reinterpret_cast<gsl::byte *>(src_buffer.ptr), src_buffer.size * src_buffer.itemsize),
[=](gsl::byte *) { arr.dec_ref(); })
.unwrap_or_throw();
arr.inc_ref();
return tensor;
})
.def("copy_to", [](runtime_tensor &from, runtime_tensor &to) {
from.copy_to(to).unwrap_or_throw();
})
.def("to_numpy", [](runtime_tensor &tensor) {
auto host = tensor.as_host().unwrap_or_throw();
auto src_map = std::move(hrt::map(host, hrt::map_read).unwrap_or_throw());
auto src_buffer = src_map.buffer();
return py::array(
to_dtype(tensor.datatype()),
tensor.shape(),
to_py_strides(runtime::get_bytes(tensor.datatype()), tensor.strides()),
src_buffer.data());
})
.def_property_readonly("dtype", [](runtime_tensor &tensor) {
return to_dtype(tensor.datatype());
})
.def_property_readonly("shape", [](runtime_tensor &tensor) {
return to_py_shape(tensor.shape());
});Each property is described below
| Property name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| dtype | int | not | Tensor's data type |
| shape | list | not | The shape of tensor |
Feature description
Construct the RuntimeTensor object from numpy.ndarray
Interface definition
from_numpy(py::array arr)Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| arr | numpy.ndarray | be | numpy.ndarray object |
The return value
RuntimeTensor
Code example
tensor = nncase.RuntimeTensor.from_numpy(self.inputs[i]['data'])Feature description
Copy Runtime Tensor
Interface definition
copy_to(RuntimeTensor to)Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| to | RuntimeTensor | be | RuntimeTensor object |
The return value
N/A
Code example
sim.get_output_tensor(i).copy_to(to)Feature description
Convert RuntimeTensor to a numpy.ndarray object
Interface definition
to_numpy()Input parameters
N/A
The return value
numpy.ndarray object
Code example
arr = sim.get_output_tensor(i).to_numpy()Feature description
Simulator class for inference kmodel on PC
Class definition
py::class_<interpreter>(m, "Simulator")
.def(py::init())
.def("load_model", [](interpreter &interp, gsl::span<const gsl::byte> buffer) { interp.load_model(buffer).unwrap_or_throw(); })
.def_property_readonly("inputs_size", &interpreter::inputs_size)
.def_property_readonly("outputs_size", &interpreter::outputs_size)
.def("get_input_desc", &interpreter::input_desc)
.def("get_output_desc", &interpreter::output_desc)
.def("get_input_tensor", [](interpreter &interp, size_t index) { return interp.input_tensor(index).unwrap_or_throw(); })
.def("set_input_tensor", [](interpreter &interp, size_t index, runtime_tensor tensor) { return interp.input_tensor(index, tensor).unwrap_or_throw(); })
.def("get_output_tensor", [](interpreter &interp, size_t index) { return interp.output_tensor(index).unwrap_or_throw(); })
.def("set_output_tensor", [](interpreter &interp, size_t index, runtime_tensor tensor) { return interp.output_tensor(index, tensor).unwrap_or_throw(); })
.def("run", [](interpreter &interp) { interp.run().unwrap_or_throw(); });Each property is described below
| Property name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| inputs_size | int | not | Enter the number of |
| outputs_size | int | not | The number of outputs |
Code example
Instantiate the Simulator
sim = nncase.Simulator()Feature description
Load the kmodel
Interface definition
load_model(model_content)Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| model_content | byte[] | be | Kmodel byte stream |
The return value
N/A
Code example
sim.load_model(kmodel)Feature description
Gets the description of the input for the specified index
Interface definition
get_input_desc(index)Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | int | be | The index of the input |
The return value
MemoryRange
Code example
input_desc_0 = sim.get_input_desc(0)Feature description
Gets the description of the output of the specified index
Interface definition
get_output_desc(index)Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | int | be | The index of the output |
The return value
MemoryRange
Code example
output_desc_0 = sim.get_output_desc(0)Feature description
Gets the RuntimeTensor for the input for the specified index
Interface definition
get_input_tensor(index)Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | int | be | Enter the index of the tensor |
The return value
RuntimeTensor
Code example
input_tensor_0 = sim.get_input_tensor(0)Feature description
Sets the Runtime Tensor for the input of the specified index
Interface definition
set_input_tensor(index, tensor)Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | int | be | Enter the index of RuntimeTensor |
| tensor | RuntimeTensor | be | Enter RuntimeTensor |
The return value
N/A
Code example
sim.set_input_tensor(0, nncase.RuntimeTensor.from_numpy(self.inputs[0]['data']))Feature description
Gets the Runtime Tensor for the output of the specified index
Interface definition
get_output_tensor(index)Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | int | be | Outputs the index of the RuntimeTensor |
The return value
RuntimeTensor
Code example
output_arr_0 = sim.get_output_tensor(0).to_numpy()Feature description
Sets the RuntimeTensor for the output of the specified index
Interface definition
set_output_tensor(index, tensor)Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | int | be | Outputs the index of the RuntimeTensor |
| tensor | RuntimeTensor | be | Output Runtime Tensor |
The return value
N/A
Code example
sim.set_output_tensor(0, tensor)Feature description
Run kmodel inference
Interface definition
run()Input parameters
N/A
The return value
N/A
Code example
sim.run()**Prerequisite:**mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image.py script has been compiled with the mobiletv2-7.onnx model
mobilenetv2_onnx_simu.py is located in the /path/to/nncase_sdk/examples/scripts subdirectory, which reads as follows
import os
import copy
import argparse
import numpy as np
import onnxruntime as ort
import nncase
def read_model_file(model_file):
with open(model_file, 'rb') as f:
model_content = f.read()
return model_content
def cosine(gt, pred):
return (gt @ pred) / (np.linalg.norm(gt, 2) * np.linalg.norm(pred, 2))
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(prog="nncase")
parser.add_argument("--model_file", type=str, help='original model file')
parser.add_argument("--kmodel_file", type=str, help='kmodel file')
parser.add_argument("--input_file", type=str, help='input bin file for kmodel')
args = parser.parse_args()
# create simulator
sim = nncase.Simulator()
# read kmodel
kmodel = read_model_file(args.kmodel_file)
# load kmodel
sim.load_model(kmodel)
# read input.bin
input_tensor=sim.get_input_tensor(0).to_numpy()
input = np.fromfile(args.input_file, input_tensor.dtype).reshape(input_tensor.shape)
# set input for simulator
sim.set_input_tensor(0, nncase.RuntimeTensor.from_numpy(input))
# simulator inference
nncase_results = []
sim.run()
for i in range(sim.outputs_size):
nncase_result = sim.get_output_tensor(i).to_numpy()
nncase_results.append(copy.deepcopy(nncase_result))
# cpu inference
cpu_results = []
ort_session = ort.InferenceSession(args.model_file)
input_name = ort_session.get_inputs()[0].name
output_name = ort_session.get_outputs()[0].name
cpu_results = ort_session.run([output_name], { input_name : input })
# compare
for i in range(sim.outputs_size):
cos = cosine(np.reshape(nncase_results[i], (-1)), np.reshape(cpu_results[i], (-1)))
print('output {0} cosine similarity : {1}'.format(i, cos))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()Execute the inference script
cd /path/to/nncase_sdk/examples
python3 scripts/mobilenetv2_onnx_simu.py --model_file models/mobilenetv2-7.onnx --kmodel_file tmp/mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image/test.kmodel --input_file mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image/data/input_0_0.binThe comparison of nncase simulator and CPU inference results is as follows
... ...
output 0 cosine similarity : 0.9992437958717346nncase runtime is used to load kmodel on AI devices/ set input data/ perform KPU calculations / obtain output data, etc.
Currently, only the C++ versionof APIs, related header files and static libraries are available in the nncase sdk/riscv64 directory
$ tree -L 3 riscv64/
riscv64/
├── include
│ ├── gsl
│ │ └── gsl-lite.hpp
│ ├── gsl-lite
│ │ └── gsl-lite.hpp
│ ├── mpark
│ │ ├── config.hpp
│ │ ├── in_place.hpp
│ │ ├── lib.hpp
│ │ └── variant.hpp
│ └── nncase
│ ├── functional
│ ├── kernels
│ ├── runtime
│ └── version.h
└── lib
├── cmake
│ ├── nncasefunctional
│ ├── nncase_rt_modules_k510
│ └── nncaseruntime
├── libnncase.functional.a
├── libnncase.rt_modules.k510.a
└── libnncase.runtime.a
13 directories, 10 filesTensor used to store model input/output data
Feature description
Create a runtime_tensor
Interface definition
(1) NNCASE_API result<runtime_tensor> create(datatype_t datatype, runtime_shape_t shape, memory_pool_t pool = pool_cpu_only, uintptr_t physical_address = 0) noexcept;
(2) NNCASE_API result<runtime_tensor> create(datatype_t datatype, runtime_shape_t shape, gsl::span<gsl::byte> data, bool copy, memory_pool_t pool = pool_cpu_only, uintptr_t physical_address = 0) noexcept;Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| datatype | datatype_t | be | Data type, such as dt_float32 |
| shape | runtime_shape_t | be | The shape of tensor |
| data | gsl::span<gsl::byte> | be | User-state data buffer |
| copy | bool | be | Whether to copy |
| pool | memory_pool_t | not | Memory pool type, default value is pool_cpu_only |
| physical_address | uintptr_t | not | Physical address, default value is 0 |
The return value
result<runtime_tensor>
Code example
// create input
auto in_shape = interp.input_shape(0);
auto input_tensor = host_runtime_tensor::create(dt_float32, in_shape,
{(gsl::byte *)mat.data, mat.cols * mat.rows * mat.elemSize()},
true, hrt::pool_shared).expect("cannot create input tensor");Interpreter is a running instance of the nncase runtime, which provides core functional functions such as load_model()/run()/input_tensor()/output_tensor().
Feature description
Load the kmodel model
Interface definition
NNCASE_NODISCARD result<void> load_model(gsl::span<const gsl::byte> buffer) noexcept;Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| buffer | gsl::span <const gsl::byte> |
be | kmodel buffer |
The return value
result <void>
Code example
template <class T>
std::vector<T>read_binary_file(const char *file_name)
{
std::ifstream ifs(file_name, std::ios::binary);
ifs.seekg(0, ifs.end);
size_t len = ifs.tellg();
std::vector<T> vec(len / sizeof(T), 0);
ifs.seekg(0, ifs.beg);
ifs.read(reinterpret_cast<char*>(vec.data()), len);
ifs.close();
return vec;
}
interpreter interp;
auto model = read_binary_file<unsigned char>(kmodel);
interp.load_model({(const gsl::byte *)model.data(), model.size()}).expect("cannot load model.");Feature description
Gets the number of model inputs
Interface definition
size_t inputs_size() const noexcept;Input parameters
N/A
The return value
size_t
Code example
auto inputs_size = interp.inputs_size();Feature description
Gets the number of model outputs
Interface definition
size_t outputs_size() const noexcept;Input parameters
N/A
The return value
size_t
Code example
auto outputs_size = interp.outputs_size();Feature description
Gets the shape of the model specified input
Interface definition
const runtime_shape_t &input_shape(size_t index) const noexcept;Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | size_t | be | The index of the input |
The return value
runtime_shape_t
Code example
auto in_shape = interp.input_shape(0);Feature description
Gets the shape of the specified output of the model
Interface definition
const runtime_shape_t &output_shape(size_t index) const noexcept;Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | size_t | be | The index of the output |
The return value
runtime_shape_t
Code example
auto out_shape = interp.output_shape(0);Feature description
Gets/sets the input tensor for the specified index
Interface definition
(1) result<runtime_tensor> input_tensor(size_t index) noexcept;
(2) result<void> input_tensor(size_t index, runtime_tensor tensor) noexcept;Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | size_t | be | kmodel buffer |
| tensor | runtime_tensor | be | Enter the corresponding runtime tensor |
The return value
(1) Returns the results<runtime_tensor>
(2) Returns the results <void>
Code example
// set input
interp.input_tensor(0, input_tensor).expect("cannot set input tensor");Feature description
Gets/sets the outbound tensor for the specified index
Interface definition
(1) result<runtime_tensor> output_tensor(size_t index) noexcept;
(2) result<void> output_tensor(size_t index, runtime_tensor tensor) noexcept;Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | size_t | be | |
| tensor | runtime_tensor | be | Enter the corresponding runtime tensor |
The return value
(1) Returns the results<runtime_tensor>
(2) Returns the results <void>
Code example
// get output
auto output_tensor = interp.output_tensor(0).expect("cannot get output tensor");
auto mapped_buf = std::move(hrt::map(output_tensor, hrt::map_read).unwrap_or_throw());
float *output_data = reinterpret_cast<float *>(mapped_buf.buffer().data());
auto out_shape = interp.output_shape(0);
auto it = std::max_element(output_data, output_data + compute_size(out_shape));
size_t idx = it - output_data;
std::cout << "image classification result: " << labels[idx] << "(" << *it << ")" << std::endl;Feature description
Perform kPU calculations
Interface definition
result<void> run() noexcept;Input parameters
N/A
The return value
result <void>
Code example
// run
interp.run().expect("error occurred in running model");The sample code is located at /path/to/nncase_sdk/examples/mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image
Prefix Condition
- mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image.py script has compiled the mobiletv2-7.onnx model
- Since the example relies on the OpenCV library, you need to specify the path to OpenCV in the CMakeLists .txt of the sample.
Cross-compile apps
cd /path/to/nncase_sdk/examples
./build.shFinally, generate the mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image in the out/bin directory
The k510 EVB operates on the board
Copy the following files onto the k510 EVB board
| file | remark |
|---|---|
| mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image | Cross-compile examples are generated |
| test.kmodel | Use mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image.py compile the mobiletv2-7.onnx build |
| Cat .png and labels_1000.txt | Located under the /path/to/nncase_sdk/examples/mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image/data/ subdirectory |
$ export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/mnt/zhangyang/nncase_check/lib/gomp:/mnt/zhangyang/nncase_check/lib/opencv
$ ./mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image test.kmodel cat.png labels_1000.txt
case ./mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image build at Mar 1 2022 16:31:29
interp.run() duration: 12.6642 ms
image classification result: tiger cat(9.25)nncase Functional is used to improve ease of use when users pre- and post-process models
Currently, only the C++ version of APIs is available, and the associated header files and libraries are in the riscv64 directory of the nncase sdk.
Feature description
Calculate the square, currently support input uint8/int8, output is also uint8/int8, note that the input is fixed point and the output is floating point need to set the quantization parameters.
Interface definition
public inline NNCASE_APIresult< runtime::runtime_tensor >square(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | be | input |
dtype |
datatype_t | be | Output tensor datatype |
The return value
result<runtime_tensor>
Code example
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto squared = F::square(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();Feature description
Calculate the root number value, currently support input uint8/int8, output is also uint8/int8, note that the input is fixed point and the output is floating point needs to set the quantization parameters.
Interface definition
public inline NNCASE_APIresult< runtime::runtime_tensor >sqrt(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | be | input |
dtype |
datatype_t | be | Output tensor datatype |
The return value
result<runtime_tensor>
Code example
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::sqrt(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();Feature description
Calculate the log value, the negative number of input will be converted to Nan, currently support input uint8/int8, output is also uint8/int8, note that the input is fixed point and the output is floating point needs to set the quantization parameter.
Interface definition
public inline NNCASE_APIresult< runtime::runtime_tensor >log(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | be | input |
dtype |
datatype_t | be | Output tensor datatype |
The return value
result<runtime_tensor>
Code example
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::log(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();Feature description
Calculate the exp value, currently support input uint8/int8, output is also uint8/int8, note that the input is fixed point and the output is floating point need to set the quantization parameters.
Interface definition
public inline NNCASE_APIresult< runtime::runtime_tensor >exp(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | be | input |
dtype |
datatype_t | be | Output tensor datatype |
The return value
result<runtime_tensor>
Code example
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::exp(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();Feature description
To calculate the sin value, the input uint8/int8 is currently supported, and the output is also uint8/int8, note that the quantization parameters need to be set when the input is fixed-point and the output is floating-point.
Interface definition
public inline NNCASE_APIresult< runtime::runtime_tensor >sin(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | be | input |
dtype |
datatype_t | be | Output tensor datatype |
The return value
result<runtime_tensor>
Code examples
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::sin(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();Feature description
Calculate the cos value, currently support input uint8/int8, output is also uint8/int8, note that the input is fixed point and the output is floating point needs to set the quantization parameter.
Interface definition
public inline NNCASE_APIresult< runtime::runtime_tensor >cos(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | be | input |
dtype |
datatype_t | be | Output tensor datatype |
The return value
result<runtime_tensor>
Code examples
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::cos(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();Feature description
To calculate the round value, the input uint8/int8 is currently supported, and the output is also uint8/int8, note that the quantization parameter needs to be set when the input is fixed point and the output is floating point.
Interface definition
public inline NNCASE_APIresult< runtime::runtime_tensor >round(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | be | input |
dtype |
datatype_t | be | Output tensor datatype |
The return value
result<runtime_tensor>
Code examples
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::round(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();Feature description
Calculate the frost value, currently support input uint8/int8, output is also uint8/int8, note that the input is fixed point and the output is floating point need to set the quantization parameters.
Interface definition
public inline NNCASE_APIresult< runtime::runtime_tensor >floor(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | be | input |
dtype |
datatype_t | be | Output tensor datatype |
The return value
result<runtime_tensor>
Code examples
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::floor(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();Feature description
Calculate the ceil value, currently support input uint8/int8, output is also uint8/int8, note that the input is fixed point and the output is floating point need to set the quantization parameters.
Interface definition
public inline NNCASE_APIresult< runtime::runtime_tensor >ceil(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | be | input |
dtype |
datatype_t | be | Output tensor datatype |
The return value
result<runtime_tensor>
Code examples
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::ceil(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();Feature description
Calculate the abs value, currently support input uint8/int8, output is also uint8/int8, note that the input is fixed point and the output is floating point needs to set the quantization parameters.
Interface definition
public inline NNCASE_APIresult< runtime::runtime_tensor >abs(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | be | input |
dtype |
datatype_t | be | Output tensor datatype |
The return value
result<runtime_tensor>
Code examples
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::abs(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();Feature description
Calculate the value of neg, currently support input uint8/int8, output is also uint8/int8, note that the input is fixed point and the output is floating point needs to set the quantization parameters.
Interface definition
public inline NNCASE_APIresult< runtime::runtime_tensor >neg(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | be | input |
dtype |
datatype_t | be | Output tensor datatype |
The return value
result<runtime_tensor>
Code examples
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::neg(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();Feature description
Input dt_bfloat16, dt_float32 data, output dt_int8, or dt_uint8 output
Interface definition
public inline NNCASE_APIresult< runtime::runtime_tensor >quantize(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | be | Input, type must be float32 or bfloat16 |
dtype |
datatype_t | be | Output tensor datatype |
The return value
result<runtime_tensor>
Code examples
auto quantized = F::quantize(input, dt_int8).unwrap_or_throw();Feature description
Enter uint8 or int8 input, convert to float or bfloat data. Note that the user must set the correct quantization parameters for the data in advance for dequantization.
Interface definition
public inline NNCASE_APIresult< runtime::runtime_tensor >dequantize(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | be | input |
dtype |
datatype_t | be | Output tensor datatype |
The return value
result<runtime_tensor>
Code examples
input.quant_param({ 0, 1 });
auto dequantized = F::dequantize(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();Feature description
Given bboxes, cropped from the original tensor and resize output into the new tensor. Accept dt_bfloat16, dt_float32, dt_int8, dt_uint8 type output, output of the same type.
Interface definition
NNCASE_API inline result<runtime::runtime_tensor> crop(runtime::runtime_tensor &input, runtime::runtime_tensor &bbox, size_t out_h, size_t out_w, image_resize_mode_t resize_mode, bool align_corners, bool half_pixel_centers) noexcept
Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| input | runtime_tensor | be | Enter the data, need to [n,c,h,w] format the layout, if the data is uint8 or int8 please ensure the correctness of the data quantization parameters |
| bbox | runtime_tensor | be | Enter the bbox data, need to [1,1,m,4] format the layout, the internal data is[y0,x0,y1,x1], the type is[float32,bfloat16] |
| out_h | size_t | be | Output data height |
| out_w | size_t | be | Enter the data width |
| resize_mode | image_resize_mode_t | be | Resize method pattern |
| align_corners | bool | be | Resize whether align_corners |
| half_pixel_centers | bool | be | Resize if the pixel is center aligned |
The return value
result<runtime_tensor>
Code examples
auto bbox = get_rand_bbox(input_shape, roi_amount);
auto &&[out_h, out_w] = get_rand_out_hw();
auto output_opt = F::crop(input, bbox, out_h, out_w, resize_mode).unwrap_or_throw();Feature description
Given the output height width, put the input tensor resize to the new size. Accept dt_bfloat16, dt_float32, dt_int8, dt_uint8 type output, output of the same type.
Interface definition
NNCASE_API inline result<runtime::runtime_tensor> resize(runtime::runtime_tensor &input, size_t out_h, size_t out_w, image_resize_mode_t resize_mode, bool align_corners, bool half_pixel_centers) noexcept
Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| input | runtime_tensor | be | Enter the data, need to be [n,c,h,w] formatted, if the data is uint8 or int8 please ensure the correctness of the data quantization parameters |
| out_h | size_t | be | Output data height |
| out_w | size_t | be | Enter the data width |
| resize_mode | image_resize_mode_t | be | Resize method pattern |
| align_corners | bool | be | Resize whether align_corners |
| half_pixel_centers | bool | be | Resize if the pixel is center aligned |
The return value
result<runtime_tensor>
Code examples
auto &&[out_h, out_w] = get_rand_out_hw();
auto output_opt = F::resize(input, out_h, out_w, resize_mode, false, false).unwrap_or_throw();Feature description
Padding data on each dimension accepts dt_bfloat16, dt_float32, dt_int8, dt_uint8 type output and output of the same type.
Interface definition
NNCASE_API inline result<runtime::runtime_tensor> pad(runtime::runtime_tensor &input, runtime_paddings_t &paddings, pad_mode_t pad_mode, float fill_v)
Input parameters
| Parameter name | type | Yes or no | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| input | runtime_tensor | be | Enter the data, if the data is uint8 or int8 Ensure the correctness of the data quantization parameters |
| padding | runtime_paddings_t | be | For example, the padding value is [ {2,3}, {1,3} ]indicated in front of pad 2 in the last dimension, followed by pad 3. The penultimate dimension is preceded by pad 1, followed by pad 2 |
| pad_mode | pad_mode_t | be | Currently, only const mode is supported |
| fill_v | float | be | Populate the values |
The return value
result<runtime_tensor>
Code examples
runtime_paddings_t paddings{ { 0, 0 }, { 0, 0 }, { 0, 0 }, { 1, 2 } };
auto output = F::pad(input, paddings, pad_constant, pad_value).unwrap_or_throw();| Classification model | CPU Precision (Top-1) | Floating-point accuracy (Top-1) | uint8 precision (Top-1) | int8 Precision (Top-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| alexnet | 0.531 | 0.53 | N/A | 0.52 |
| densenet 121 | 0.732 | 0.732 | 0.723 | N/A |
| inception v3 | 0.766 | 0.765 | 0.773 | 0.77 |
| inception v4 | 0.789 | 0.789 | 0.793 | 0.792 |
| mobilenet v1 | 0.731 | 0.73 | 0.723 | 0.718 |
| mobilenet v2 | 0.713 | 0.715 | 0.713 | 0.719 |
| resnet50 v2 | 0.747 | 0.74 | 0.748 | 0.749 |
| vgg 16 | 0.689 | 0.687 | 0.690 | 0.689 |
This table is mainly to compare the performance of quantization, the CPU precision is the full ImageNet validation set data, and the floating-point and quantization accuracy is the result of the data subset test for the first image of the 1000 classes in the validation set according to the ordinal number.
The test results of Alexnet and SenseNet are old data, both of which are test results of the first 1000 images of the verification set as a subset of the data, and N/A is that the test data subset at that time is different from the CPU, so it is not used as a comparison.
Because the selected network does not necessarily originate from the official or there are differences in pre-processing, etc., it may differ from the official performance.
-
YOLOV3
COCOAPI Official results CPU floating-point precision gnne floating-point precision uint8 precision int8 precision Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 100] 0.314 0.307 0.306 0.295 0.288 Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50| area = all | maxDets = 100] 0.559 0.555 0.554 0.555 0.554 Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.75| area = all | maxDets = 100] 0.318 0.308 0.307 0.287 0.275 Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = small | maxDets = 100] 0.142 0.150 0.149 0.147 0.144 Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = medium | maxDets = 100] 0.341 0.332 0.332 0.322 0.316 Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = large | maxDets = 100] 0.464 0.437 0.437 0.414 0.404 Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 1] 0.278 0.270 0.271 0.262 0.256 Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 10] 0.419 0.412 0.412 0.399 0.392 Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 100] 0.442 0.433 0.433 0.421 0.414 Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = small | maxDets = 100] 0.239 0.251 0.251 0.248 0.246 Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = medium | maxDets = 100] 0.482 0.462 0.463 0.451 0.443 Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = large | maxDets = 100] 0.611 0.586 0.585 0.559 0.550 -
ssd-mobilenetv1
COCOAPI Official results CPU floating-point precision gnne floating-point precision uint8 precision int8 precision Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 100] 0.184 0.184 0.184 0.183 0.183 Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50| area = all | maxDets = 100] 0.306 0.307 0.306 0.305 0.306 Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.75| area = all | maxDets = 100] 0.191 0.192 0.190 0.189 0.190 Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = small | maxDets = 100] 0.017 0.017 0.017 0.017 0.017 Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = medium | maxDets = 100] 0.157 0.157 0.157 0.156 0.155 Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = large | maxDets = 100] 0.371 0.372 0.371 0.370 0.369 Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 1] 0.180 0.180 0.180 0.181 0.181 Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 10] 0.242 0.242 0.242 0.243 0.243 Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 100] 0.242 0.242 0.242 0.243 0.243 Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = small | maxDets = 100] 0.026 0.026 0.026 0.026 0.026 Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = medium | maxDets = 100] 0.206 0.206 0.206 0.206 0.205 Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = large | maxDets = 100] 0.489 0.491 0.490 0.490 0.491 -
YOLOV5S
COCOAPI Official results CPU floating-point precision gnne floating-point precision uint8 precision int8 precision Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 100] 0.367 0.365 0.335 0.334 0.335 Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50| area = all | maxDets = 100] 0.555 0.552 0.518 0.518 0.518 Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.75| area = all | maxDets = 100] 0.398 0.395 0.364 0.363 0.362 Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = small | maxDets = 100] 0.223 0.220 0.199 0.199 0.197 Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = medium | maxDets = 100] 0.419 0.418 0.387 0.386 0.386 Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = large | maxDets = 100] 0.463 0.459 0.423 0.422 0.423 Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 1] 0.306 0.306 0.288 0.287 0.287 Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 10] 0.518 0.518 0.487 0.486 0.487 Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 100] 0.576 0.576 0.540 0.539 0.540 Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = small | maxDets = 100] 0.391 0.399 0.350 0.350 0.347 Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = medium | maxDets = 100] 0.641 0.640 0.606 0.605 0.607 Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = large | maxDets = 100] 0.716 0.710 0.680 0.683 0.685
-
安装wheel时报错: "xxx.whl is not a supported wheel on this platform." **
Q: 安装nncase wheel包, 出现ERROR: nncase-1.0.0.20210830-cp37-cp37m-manylinux_2_24_x86_64.whl is not a supported wheel on this platform.
A: Upgrade pip > = 20.3
sudo pip3 install --upgrade pip
-
When the CRB runs the App inference program, it reports the error "std::bad_alloc"
Q: Run the App inference program on the CRB and throw a "std::bad_alloc" exception
$ ./cpp.sh case ./yolov3_bfloat16 build at Sep 16 2021 18:12:03 terminate called after throwing an instance of 'std::bad_alloc' what(): std::bad_alloc
A: std::bad_alloc exceptions are usually caused by memory allocation failures, which can be checked as follows.
- Check whether the generated kmodel exceeds the current system available memory (such as yolov3 bfloat16 kmodel size is 121MB, the current Linux available memory is only 70MB, the exception will be thrown). If it exceeds, try using post-training quantization to reduce the kmodel size.
- Check the app for memory leaks
-
When running the App inference program[.. t_runtime_tensor.cpp:310 (create)] data.size_bytes() == size = false (bool).
Q: Simulator runs the App inference program, throwing a "[.. t_runtime_tensor.cpp:310 (create)] data.size_bytes() == size = false (bool)" exception
A: Check the input tensor information for the settings, focusing on the input shape and the number of bytes occupied by each element (fp32/uint8)
Translation Disclaimer
For the convenience of customers, Canaan uses an AI translator to translate text into multiple languages, which may contain errors. We do not guarantee the accuracy, reliability or timeliness of the translations provided. Canaan shall not be liable for any loss or damage caused by reliance on the accuracy or reliability of the translated information. If there is a content difference between the translations in different languages, the Chinese Simplified version shall prevail.
If you would like to report a translation error or inaccuracy, please feel free to contact us by mail.