This Package is currently unmaintained. For streaming audio input and output see PortAudio.jl.
As of May 1, 2020 PortAudio.jl doesn't support JACK, but adding JACK support to it is probably a better path forward than maintaining JACKAudio.jl separately. See this issue on adding JACK support to PortAudio.jl for more details.
This package allows Julia software to read and write audio through the JACK Audio Connection Kit, a cross-platform, low-latency audio system. The goal is to be able to easily interface with JACK using the SampleSink/SampleSource API defined in SampledSignals.jl, not necessarily to create a full-featured JACK library (though PRs are welcome to wrap more of libjack).
The package is tested against both JACK1 and JACK2, and on OSX and Linux.
To use this package you must have a working JACK installation. For linux this is most likely available through your distribution. On OSX you can download JACKOSX binaries. JACKAudio.jl is mostly tested with JACK2, but should also work with JACK1. We also recommend that you have some sort of JACK routing tool such as QjackCtl to configure and start the JACK server and connect your applications to each other. JACKAudio.jl can start up a jack server in the background if there isn't one already running, but does not expose more advanced configuration, so you're better off using a separate tool to manage your JACK server process.
A JACKClient represents a connection to the JACK server, and serves as a container for some number of JACKSources and JACKSinks. Each JACKSource represents a logically-distinct multi-channel stream. It is a "Source" from the perspective of your Julia code, and acts as an input to your JACKClient. Likewise JACKSink is an output.
In JACK the channels of a JACKSource called "out" would be given the names "out_1", and "out_2". As an example, a JACKClient implementing a stereo reverb might have a single 2-channel JACKSource input, whereas a mono compressor with a side-chain input might have two mono JACKSources. JACKSource is a subtype of the AudioSource abstract type defined in SampledSignals.jl.
The default JACKClient is named "Julia" and has one stereo input source and one stereo output sink. You can instantiate it like so:
c = JACKClient()or give it a different name
c = JACKClient("Verberator2000")You can specify the number of channels for the default source and sink:
c = JACKClient("QuadIO", 4, 4) # also works without specifying the nameThe full constructor call allows you to create multiple sources/sinks with different names and channel counts:
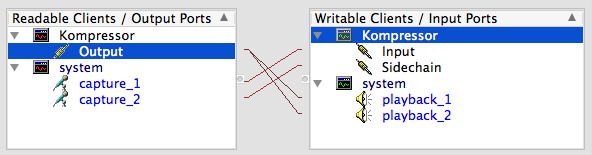
c = JACKClient("Kompressor", [("Input", 1), ("Sidechain", 1)], [("Output", 1)])After wiring up the inputs and outputs in QjackCtl, you would end up with this:
You can access the sources and sinks of a JACKClient with the sources and sinks methods:
c = JACKClient()
source = sources(c)[1]
sink = sinks(c)[1]Interfacing with JACK sources and sinks is best done with SampleBufs, from the SampledSignals.jl package, which handles type and samplerate conversions, as well as convenience features like indexing by time. For instance, to read 5 seconds of audio and play it back, you can write:
using SampledSignals
buf = read(source, 5s)
write(sink, buf)Because the common case is to have a JACKClient with exactly one source and one sink, JACKAudio implements wrapper functions for read!, read, and write that pass any arguments through to the first sink or source, so the above example could become:
c = JACKClient()
buf = read(c, 5s)
write(c, buf)