Let's make this repository full of interview questions!
This repository is maintained by LetsDefend. If you think any interview question is missing or incorrect, please feel free to submit a pull request (PR) to this repo. We will review the PR and merge if appropriate.
- What should you expect?
- Security Analyst
- Incident Response
- Pre-preparing
- General
- Network
- Web Application Security
- Cryptography
- Malware Analysis
- Event Log Analysis
- Threat Intelligence
Below is a list of the topics on which questions can be asked in the interview.
- Basic terminologies
- Network fundamentals
- Operating system fundamentals
- Malware analysis fundamentals
- How to analyze attacks (phishing, malware...)
- Incident response procedure
- How to detect and remediate specific kind of attack (like golden ticket, phishing etc.)
- Ransomware remediation process
- First, fully understand what kind of role you are applying for. Like if you're applying Security Analyst (Tier 1 Analyst) job, then you should already know what Security Analysts do or what difficulties SOC Analysts are having.
- Make sure that you know about the company you are applying for. Are you going to give support multiple companies at the same time or they are looking for internal SOC?
- If you have any friend who is working at the company you're applying for, make a phone call and ask what kind of difficulties your friend is having.
- Do not tell your salary expectation on interview. Answer like: "I think my salary expectations are within your scale. In case of positive progress, I am open to your suggestions at the proposal stage."
- Make sure you know the salary scale of the job you're applying. You can ask on Reddit.
- Reading daily infosec news from different resources.
- By following infosec related social media accounts.
- Telegram channels
- Joining newsletters related to cyber security
Black-Hat Hackers: Those hackers who enter the system without taking owners’ permission. These hackers use vulnerabilities as entry points. They hack systems illegally. They use their skills to deceive and harm people. (GeeksforGeeks)
White-Hat Hackers: Also known as Ethical Hackers. They are certified hackers who learn hacking from courses. These are good hackers who try to secure our data, websites. With the rise of cyberattacks organizations and governments have come to understand that they need ethical hackers. (GeeksforGeeks)
Gray-Hat Hackers: A mix of both Black-Hat and White-Hat hackers. These types of hackers find vulnerabilities in systems without the permission of owners. They don’t have any malicious intent. However, this type of hacking is still considered illegal. But they never share information with black hat hackers. They find issues and report the owner, sometimes requesting a small amount of money to fix it. (GeeksforGeeks)
Port scanning is a method of determining which ports on a network are open and could be receiving or sending data. It is also a process for sending packets to specific ports on a host and analyzing responses to identify vulnerabilities. (Avast)
While this question is up to you, having a basic understanding of programming languages can be a plus for the interview.
Red team is attacker side, blue team is defender side.
Firewall is a device that allows or blocks the network traffic according to the rules.
It is a security vulnerability caused by incomplete or incorrect configuration.
Vulnerability: Weakness in an information system, system security procedures, internal controls, or implementation that could be exploited or triggered by a threat source. (src: NIST)
Risk: The level of impact on agency operations (including mission functions, image, or reputation), agency assets, or individuals resulting from the operation of an information system given the potential impact of a threat and the likelihood of that threat occurring. (src: NIST)
Threat: Any circumstance or event with the potential to adversely impact organizational operations, organizational assets, individuals, other organizations, or the Nation through a system via unauthorized access, destruction, disclosure, modification of information, and/or denial of service. (src: NIST)
Following the set of standards authorized by an organization, independent part, or government.
MITRE ATT&CK® is a globally-accessible knowledge base of adversary tactics and techniques based on real-world observations. The ATT&CK knowledge base is used as a foundation for the development of specific threat models and methodologies in the private sector, in government, and in the cybersecurity product and service community. (MITRE ATT&CK)
If you do have any project to show, make sure that you prepare it before the interview.
2FA is an extra layer of security used to make sure that people trying to gain access to an online account are who they say they are. First, a user will enter their username and password. Then, instead of immediately gaining access, they will be required to provide another piece of information. (Authy)
- Antivirus
- EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response)
- XDR (Extended Detection and Response)
- DLP (Data Loss Prevention)
-
HIDS: HIDS means Host Intrusion Detection System. HIDS is located on each host.
-
NIDS: NIDS means Network Intrusion Detection System. NIDS is located in the network.
The three letters in "CIA triad" stand for Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. The CIA triad is a common model that forms the basis for the development of security systems. They are used for finding vulnerabilities and methods for creating solutions. (Fortinet)
Confidentiality: Confidentiality involves the efforts of an organization to make sure data is kept secret or private. A key component of maintaining confidentiality is making sure that people without proper authorization are prevented from accessing assets important to your business.
Integrity: Integrity involves making sure your data is trustworthy and free from tampering. The integrity of your data is maintained only if the data is authentic, accurate, and reliable.
Availability: Systems, networks, and applications must be functioning as they should and when they should. Also, individuals with access to specific information must be able to consume it when they need to, and getting to the data should not take an inordinate amount of time.
Authentication: Authentication involves a user providing information about who they are. Users present login credentials that affirm they are who they claim. (Fortinet)
Authorization: Authorization follows authentication. During authorization, a user can be granted privileges to access certain areas of a network or system. (Fortinet)
Accounting: Accounting keeps track of user activity while users are logged in to a network by tracking information such as how long they were logged in, the data they sent or received, their Internet Protocol (IP) address, the Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) they used, and the different services they accessed. (Fortinet)
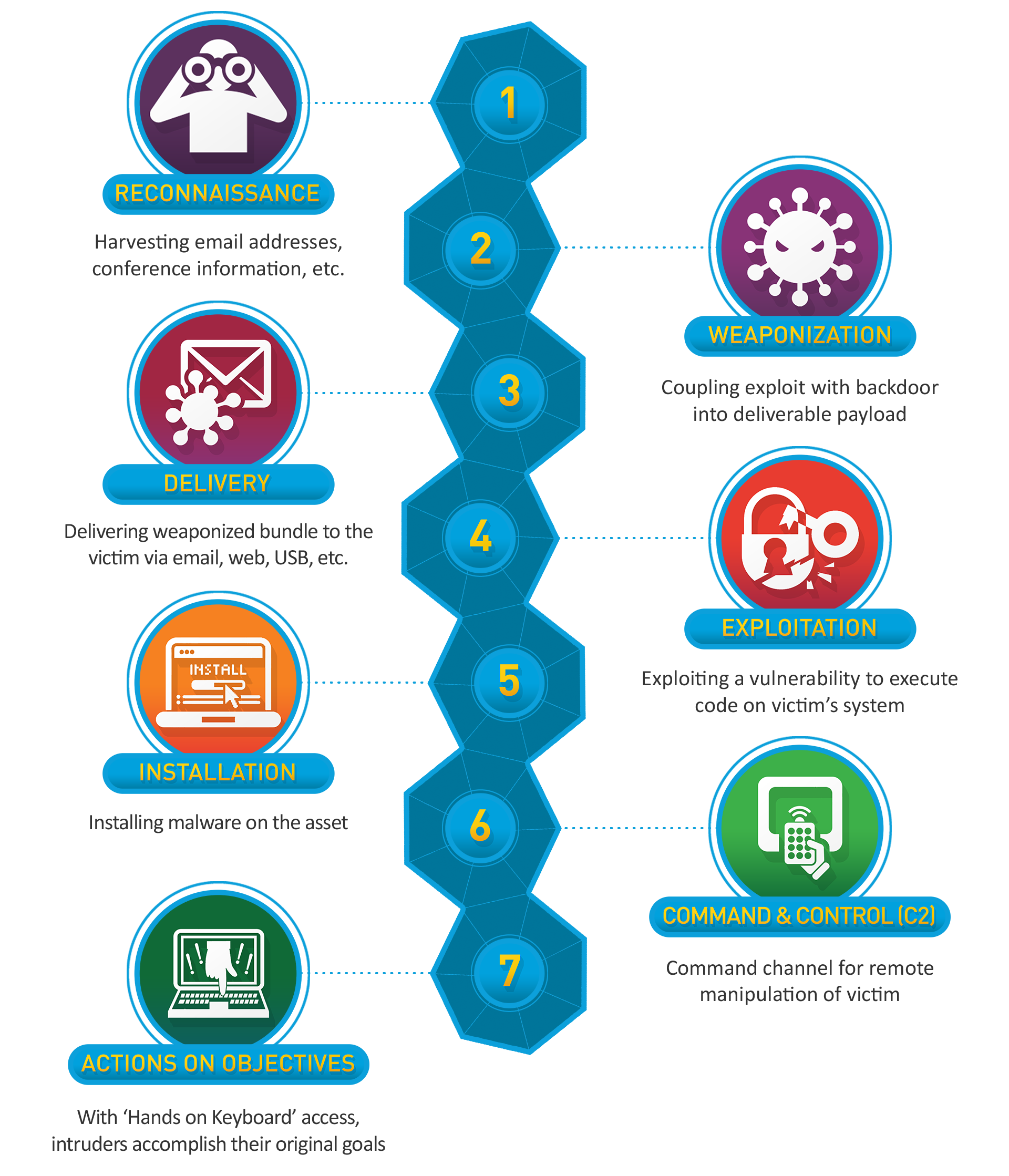
Developed by Lockheed Martin, the Cyber Kill Chain® framework is part of the Intelligence Driven Defense® model for identification and prevention of cyber intrusions activity. The model identifies what the adversaries must complete in order to achieve their objective.
The seven steps of the Cyber Kill Chain® enhance visibility into an attack and enrich an analyst’s understanding of an adversary’s tactics, techniques and procedures. (Lockheed Martin)
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), is a security solution that provides the real time logging of events in an environment. The actual purpose for event logging is to detect security threats.
In general, SIEM products have a number of features. The ones that interest us most as SOC analysts are: they filter the data that they collect and create alerts for any suspicious events. (LetsDefend)
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) serve as forensic evidence of potential intrusions on a host system or network. These artifacts enable Information Security (InfoSec) professionals and system administrators to detect intrusion attempts or other malicious activities. Security researchers use IOCs to better analyze a particular malware’s techniques and behaviors. IOCs also provides actionable threat intelligence that can be shared within the community to further improve an organization’s incident response and remediation strategies. (TrendMico)
Indicators of Attack (IOAs) demonstrate the intentions behind a cyberattack and the techniques used by the threat actor to accomplish their objectives. The specific cyber threats arming the attack, like malware, ransomware, or advanced threats, are of little concern when analyzing IOAs. (UpGuard)
True Positive:
If the situation to be detected and the detected (triggered alert) situation are the same, it is a True Positive alert. For example, let's say you had a PCR test to find out whether you are Covid19 positive and the test result came back positive. It is True Positive because the condition you want to detect (whether you have Covid19 disease) and the detected condition (being a Covid19 patient) are the same. This is a true positive alert. (LetsDefend)
Let’s suppose there is a rule to detect SQL Injection attacks and this rule has been triggered because of a request that was made to the following URL. The alert is indeed a “True Positive” as there was a real SQL Injection attack.
https://app.letsdefend.io/casemanagement/casedetail/115/src=' OR 1=1
False Positive:
In short, it is a false alarm. For example, there is a security camera in your house and if the camera alerts you due to your cat's movements, it is a false positive alert. (LetsDefend)
If we look at the URL example below, we see the SQL parameter "Union" keyword within this URL. If an SQL injection alert occurs for this URL, it will be a false positive alert because the “Union” keyword is used to mention a sports team here and not for an SQL injection attack.
https://www.google.com/search?q=FC+Union+Berlin
The Zero Trust security model is a cybersecurity framework that operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify." It assumes that threats can come from both outside and inside the network and thus requires strict identity verification for every person and device trying to access resources on the network, regardless of whether they are within or outside the network perimeter.
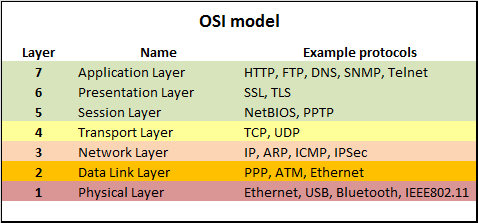
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model is a conceptual model that describes the universal standard of communication functions of a telecommunication system or computing system, without any regard to the system's underlying internal technology and specific protocol suites. (Wikipedia)
-
Physical Layer: The Physical Layer is responsible for the transmission and reception of unstructured raw data between a device, such as a network interface controller, Ethernet hub or network switch and a physical transmission medium. It converts the digital bits into electrical, radio, or optical signals.
-
Data Link Layer: The Data Link Layer provides node-to-node data transfer a link between two directly connected nodes. It detects and possibly corrects errors that may occur in the physical layer. It defines the protocol to establish and terminate a connection between two physically connected devices. It also defines the protocol for flow control between them. IEEE 802 divides the Data Link Layer into two sublayers:
-
Medium Access Control (MAC) Layer – responsible for controlling how devices in a network gain access to a medium and permission to transmit data.
-
Logical Link Control (LLC) Layer – responsible for identifying and encapsulating network layer protocols, and controls error checking and frame synchronization.
-
-
Network Layer: The Network Layer provides the functional and procedural means of transferring packets from one node to another connected in "different networks".
-
Transport Layer: The Transport Layer provides the functional and procedural means of transferring variable-length data sequences from a source host to a destination host from one application to another across a network, while maintaining the Quality of Service (QoS) functions. Transport protocols may be connection-oriented or connectionless.
-
Session Layer: The Session Layer creates the setup, controls the connections, and ends the teardown, between two or more computers, which is called a "session". Since DNS and other Name Resolution Protocols operate in this part of the layer, common functions of the session layer include user logon (establishment), name lookup (management), and user logoff (termination) functions. Including this matter, authentication protocols are also built into most client software, such as FTP Client and NFS Client for Microsoft Networks. Therefore, the session layer establishes, manages and terminates the connections between the local and remote application.
-
Presentation Layer: The Presentation Layer establishes data formatting and data translation into a format specified by the application layer during the encapsulation of outgoing messages while being passed down the protocol stack, and possibly reversed during the deencapsulation of incoming messages when being passed up the protocol stack. For this very reason, outgoing messages during encapsulation are converted into a format specified by the application layer, while the conversation for incoming messages during deencapsulation are reversed.
-
Application layer: The Application Layer is the layer of the OSI model that is closest to the end user, which means both the OSI application layer and the user interact directly with software application that implements a component of communication between the client and server, such as File Explorer and Microsoft Word. Such application programs fall outside the scope of the OSI model unless they are directly integrated into the Application layer through the functions of communication, as is the case with applications such as Web Browsers and Email Programs. Other examples of software are Microsoft Network Software for File and Printer Sharing and Unix/Linux Network File System Client for access to shared file resources.
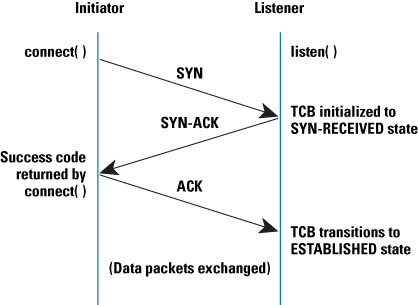
TCP uses a three-way handshake to establish a reliable connection. The connection is full duplex, and both sides synchronize (SYN) and acknowledge (ACK) each other.
The client chooses an initial sequence number, set in the first SYN packet. The server also chooses its own initial sequence number, set in the SYN/ACK packet.
Each side acknowledges each other's sequence number by incrementing it; this is the acknowledgement number. The use of sequence and acknowledgment numbers allows both sides to detect missing or out-of-order segments.
Once a connection is established, ACKs typically follow for each segment. The connection will eventually end with a RST (reset or tear down the connection) or FIN (gracefully end the connection). (ScienceDirect)
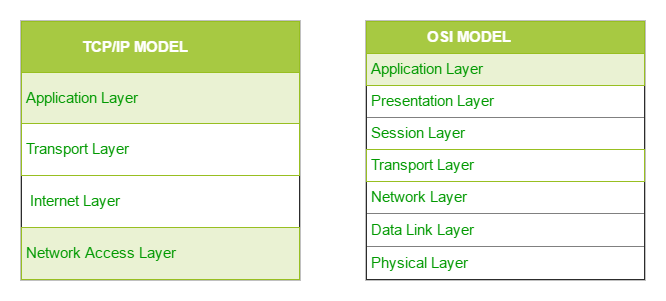
The TCP/IP model is the default method of data communication on the Internet. It was developed by the United States Department of Defense to enable the accurate and correct transmission of data between devices.
TCP/IP divides communication tasks into layers that keep the process standardized, without hardware and software providers doing the management themselves. The data packets must pass through four layers before they are received by the destination device, then TCP/IP goes through the layers in reverse order to put the message back into its original format. (Fortinet)
TCP/IP Model contains four layers. The layers are:
- Application Layer
- Transport Layer
- Internet Layer
- Network Access Layer
Differences:
| TCP/IP | OSI |
|---|---|
| TCP refers to Transmission Control Protocol | OSI refers to Open Systems Interconnection |
| TCP/IP has 4 layers | OSI has 7 layers |
| TCP/IP uses both session and presentation layer in the application layer itself | OSI uses different session and presentation layers |
| TCP/IP developed protocols then model | OSI developed model then protocol |
| (GeeksforGeeks) |
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a communication protocol used for discovering the Data Link Layer address, such as a MAC address, associated with a given Network Layer address, typically an IPv4 address. This mapping is a critical function in the Internet protocol suite. (Wikipedia)
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network management protocol used on Internet Protocol (IP) networks for automatically assigning IP addresses and other communication parameters to devices connected to the network using a client–server architecture.
- Firewall
- IDS (Intrusion Detection System)
- IPS (Intrusion Prevention System)
- WAF (Web Application Firewall)
IDS only detects the traffic but IPS can prevent/block the traffic.
While answering this question vary different scenarios, encryption is the key point for being safe.
Kerberos is a network authentication protocol that uses secret-key cryptography to authenticate users and services in a network environment. It's designed to provide strong authentication for client/server applications by verifying the identity of users and services without transmitting passwords over the network.

When the user wants to access a specific service, they contact the Ticket Granting Service (TGS) with their TGT, requesting access. The TGS decrypts the TGT, verifies its validity, and issues a service ticket that's encrypted with the service's secret key.
The user then presents this service ticket to the desired network service. The service decrypts the ticket using its own secret key, verifies the ticket's validity, and if everything is correct, grants access to the user.
An attacker gains access to a domain's Key Distribution Center service account, allowing them to create authentication tickets granting unauthorized access to any resource within the domain.
- 1XX: Informational
- 2XX: Success
- 3XX: Redirection
- 4XX: Client-Side Error
- 5XX: Server-Side Error
For example, 404 is 'server cannot find the requested resource'.
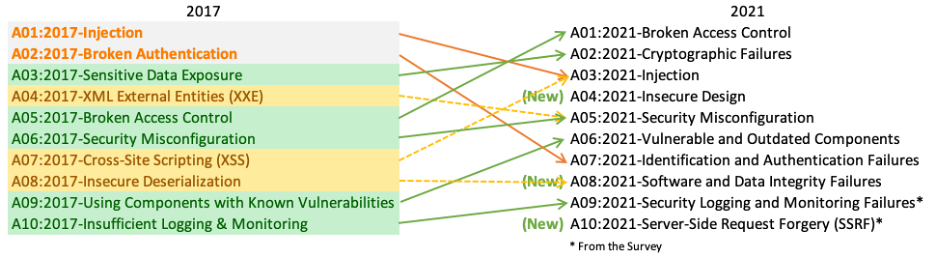
The OWASP Top 10 is a standard awareness document for developers and web application security. It represents a broad consensus about the most critical security risks to web applications. (OWASP)
SQL Injections are critical attack methods where a web application directly includes unsanitized data provided by the user in SQL queries. (LetsDefend)
There are 3 types of SQL Injections. These are:
-
In-Band SQLi (Classical SQLi): If a SQL query is sent and a replied to over the same channel, we call these In-band SQLi. It is easier for attackers to exploit these compared to other SQLi categories.
-
Inferential SQLi (Blind SQLi): SQL queries that receive a reply that cannot be seen are called Inferential SQLi. They are called Blind SQLi because the reply cannot be seen.
-
Out-of-Band SQLi: If the reply to a SQL query is communicated over a different channel then this type of SQLi is called Out-of-Band SQLi. For example, if the attacker is receiving replies to his SQL queries over the DNS this is called an Out-of-Band SQLi.
-
When examining a web request check all areas that come from the user: Because SQL Injection attacks are not limited to the form areas, you should also check the HTTP Request Headers like User-Agent.
-
Look for SQL keywords: Look for words like INSERT, SELECT, WHERE within the data received from users.
-
Check for special characters: Look for apostrophes (‘), dashes (-), or parentheses which are used in SQL or special characters that are frequently used in SQL attacks within the data received from the user.
-
Familiarize yourself with frequently used SQL Injection payloads: Even though SQL payloads change according to the web application, attackers still use some common payloads to check for SQL Injection vulnerabilities. If you are familiar with these payloads, you can easily detect SQL Injection payloads. You can see some frequently used SQL Injection payloads here.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks are a type of injection, in which malicious scripts are injected into otherwise benign and trusted websites. XSS attacks occur when an attacker uses a web application to send malicious code, generally in the form of a browser side script, to a different end user. Flaws that allow these attacks to succeed are quite widespread and occur anywhere a web application uses input from a user within the output it generates without validating or encoding it. (OWASP)
For XSS attacks to be successful, an attacker needs to insert and execute malicious content in a webpage. Each variable in a web application needs to be protected. Ensuring that all variables go through validation and are then escaped or sanitized is known as perfect injection resistance. Any variable that does not go through this process is a potential weakness. Frameworks make it easy to ensure variables are correctly validated and escaped or sanitized.
However, frameworks aren't perfect and security gaps still exist in popular frameworks like React and Angular. Output Encoding and HTML Sanitization help address those gaps.
-
Reflected XSS (Non-Persistent): It is a non-persistent XSS type that the XSS payload must contain in the request. It is the most common type of XSS.
-
Stored XSS (Persistent): It is a type of XSS where the attacker can permanently upload the XSS payload to the web application. Compared to other types, the most dangerous type of XSS is Stored XSS.
-
DOM Based XSS: DOM Based XSS is an XSS attack wherein the attack payload is executed as a result of modifying the DOM "environment" in the victim’s browser used by the original client-side script, so that the client-side code runs in an "unexpected" manner. (OWASP)
Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR), is a vulnerability caused by the lack of an authorization mechanism or because it is not used properly. It enables a person to access an object that belongs to another.
Among the highest web application vulnerability security risks published in the 2021 OWASP, IDOR or "Broken Access Control" takes first place.
Remote File Inclusion (RFI), is the security vulnerability that occurs when a file on a different server is included without sanitizing the data obtained from a user.
Local File Inclusion (LFI), is the security vulnerability that occurs when a local file is included without sanitizing the data obtained from a user.
LFI differs from RFI because the file that is intended to be included is on the same web server that the web application is hosted on.
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) is an attack that forces an end user to execute unwanted actions on a web application in which they're currently authenticated. With a little help of social engineering (such as sending a link via email or chat), an attacker may trick the users of a web application into executing actions of the attacker's choosing. If the victim is a normal user, a successful CSRF attack can force the user to perform state changing requests like transferring funds, changing their email address, and so forth. If the victim is an administrative account, CSRF can compromise the entire web application. (OWASP)
Web Application Firewall (WAF) helps protect web applications by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic between a web application and the Internet. It typically protects web applications from attacks such as Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF), Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), file inclusion, and SQL Injection, among others. A WAF is a protocol layer 7 defense (in the OSI model), and is not designed to defend against all types of attacks. (Cloudflare)
Encoding: Converts the data in the desired format required for exchange between different systems.
Hashing: Maintains the integrity of a message or data. Any change did any day could be noticed.
Encryption: Ensures that the data is secure and one needs a digital verification code or image in order to open it or access it.
Hashing: Hashing is the process of converting the information into a key using a hash function. The original information cannot be retrieved from the hash key by any means. (GeeksforGeeks)
Encryption: Encryption is the process of converting a normal readable message known as plaintext into a garbage message or not readable message known as Ciphertext. The ciphertext obtained from the encryption can easily be transformed into plaintext using the encryption key. (GeeksforGeeks)
Differences:
-
The hash function does not need a key to operate.
-
While the length of the output can variable in encryption algorithms, there is a fixed output length in hashing algorithms.
-
Encryption is a two-way function that includes encryption and decryption whilst hashing is a one-way function that changes a plain text to a unique digest that is irreversible.
A salt is added to the hashing process to force their uniqueness, increase their complexity without increasing user requirements, and to mitigate password attacks like hash tables. (Auth0)
| SSL | TLS |
|---|---|
| SSL stands for "Secure Socket Layer". | TLS stands for "Transport Layer Security". |
| Netscape developed the first version of SSL in 1995. | The first version of TLS was developed by the Internet Engineering Taskforce (IETF) in 1999. |
| SSL is a cryptographic protocol that uses explicit connections to establish secure communication between web server and client. | TLS is also a cryptographic protocol that provides secure communication between web server and client via implicit connections. It’s the successor of SSL protocol. |
| Three versions of SSL have been released: SSL 1.0, 2.0, and 3.0. | Four versions of TLS have been released: TLS 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, and 1.3. |
| All versions of SSL have been found vulnerable, and they all have been deprecated. | TLS 1.0 and 1.1 have been “broken” and are deprecated as of March 2020. TLS 1.2 is the most widely deployed protocol version. |
| (SECTIGOStore) |
- Compiler
- Disassembler
-
Static Analysis: It is the approach of analyzing malicious software by reverse engineering methods without running them. Generally, by decompiling / disassembling the malware, each step that the malware will execute is analyzed, hence the behavior / capacity of the malware can be analyzed.
-
Dynamic Analysis: It is the approach that examines the behavior of malicious software on the system by running it. In dynamic analysis, applications that can examine registry, file, network and process events are installed in the system, and their behavior is examined by running malicious software.
Differences:
| Static Analysis | Dynamic Analysis |
|---|---|
| Static analysis takes long time. | Dynamic analysis in general takes a short while. |
| You can learn the capacity of the malware. | As a result of dynamic analysis, you can learn only the activities on the system on which it is run. |
| Detailed analysis result. | Analysis result is not detailed. |
It should also be noted that using only one approach may not be sufficient to analyze malware. Using both approaches together will give you to best results!
- Services
- Registry Run Keys (Run, RunOnce)
- Task Scheduler
- Infecting to clean files
- Security
- Application
- System
- 4624
- 4625
- You can detect an authentication activities associated with a remote user with
Event ID: 4624andLogon Type: 10orLogon Type: 7if a user is reactivating a disconnected session.
Event ID: 1149fromMicrosoft-Windows-Terminal-Services-RemoteConnectionManager
Threat intelligence is the analysis of data using tools and techniques to generate meaningful information about existing or emerging threats targeting the organization that helps mitigate risks. Threat Intelligence helps organizations make faster, more informed security decisions and change their behavior from reactive to proactive to combat the attacks. (eccouncil)
No. An IP Address can become threat intelligence if contextualised with the nature of the potential threat.
TAXII, short for Trusted Automated eXchange of Intelligence Information, defines how cyber threat information can be shared via services and message exchanges. (anomali)
- IBM X-Force Exchange
- Cisco Talos
- OTX AlienVault
- Strategic Threat Intelligence
- Tactical Threat Intelligence
- Technical Threat Intelligence
- Operational Threat Intelligence