kMSR provides various implementations to solve the k-Min-Sum-Radii problem. The k-Min-Sum-Radii problem is a clustering problem that aims to minimize the sum of the radii of the clusters. Given a set of points, the aim is to find
-
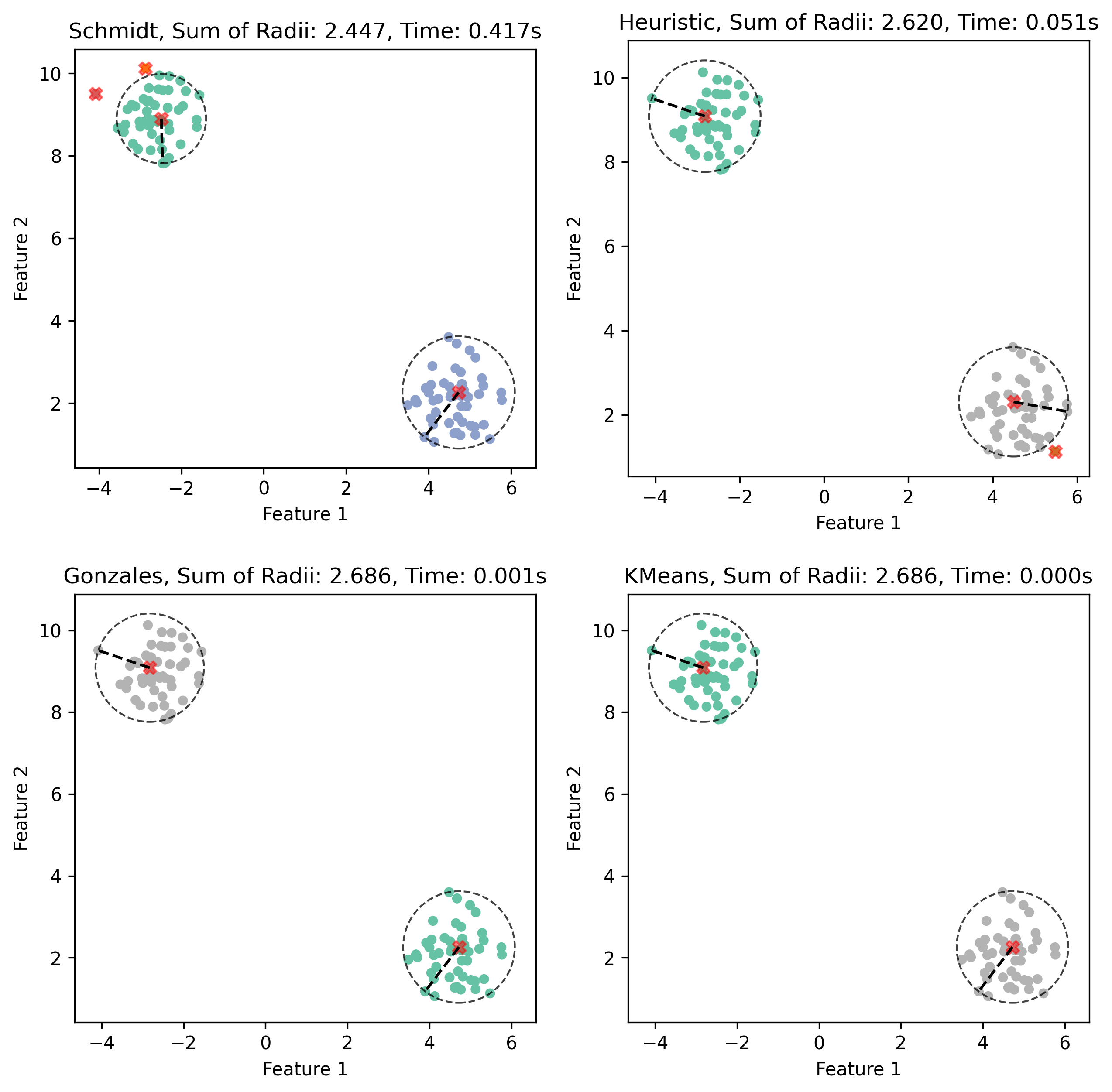
fpt-heuristic: The algorithm is an heuristic version of what is described in this paper. In practice, this works well for clusters that are not too separated. The algorithm uses the parametersepsilon,n_u, andnum_test_radiito control the trade-off between the quality of the solution and the runtime. Increasen_ufor a more accurate solution, which will however require more computation time. -
heuristic: The algorithm is a simple heuristic that explores all possible combinations for the first cluster, and then selects the remaining centers as the points farthest from the radius of the first cluster. This algorithm works well in practice but it is not practical for large datasets. -
gonzalez: This is the standard Gonzalez algorithm for$k$ -center. -
kmeans: This is the k-means++ algorithm for$k$ -means.
Although the last two algorithms are not specifically designed for the k-Min-Sum-Radii problem, they serve as useful baselines for comparing the performance of other algorithms. Additionally, an optimization has been integrated into all algorithms: intersecting balls are merged at the end, resulting in a more cost-effective solution.
For computing the minimum enclosing circle of a set of points we use the miniball header for C++. Their code has not been changed.
You can try kMSR out on our Clustering Toolkit!
We highly recommend to install OpenMP. Parts of the code are parallelized and will be much faster. However, on Windows and MacOS the code also works without OpenMP. Nonetheless, the code was written for Linux and will achieve the best performance there.
On Linux, you can use the following command:
# Alpine
sudo apk add openmp-dev libgomp
# Ubuntu
sudo apt-get install libomp-dev libgomp1
# Debian
sudo apt-get install gcc libomp-dev libomp5 libgomp1
# ArchLinux
sudo pacman -S openmp
ln -s libomp.so libomp.so.5We have tested this on docker, so it might be a little different on your system.
On MacOS, you can use the following command:
brew install llvm libompHowever, it might be that MacOS does not find the installed library. In build_extension.py, the paths are set manually. If it does not work for you, please clone the repository and run poetry build. You will see a message in red if your OpenMP is not found.
Then, you can install the package via pip:
pip install kmsrfrom kmsr import KMSR
from kmsr.plot import plot_multiple_results
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
from time import time
points, ground_truth = make_blobs(
n_samples=100,
n_features=2,
centers=2,
cluster_std=0.6,
shuffle=True,
random_state=42,
)
labels = []
centers = []
radii = []
titles = []
for algo in ["FPT-heuristic", "Heuristic", "Gonzalez", "KMeans"]:
kmsr = KMSR(
n_clusters=5,
algorithm=algo,
epsilon=0.5,
n_u=10000,
n_test_radii=10,
random_state=42,
)
start = time()
kmsr.fit(points)
end = time() - start
labels.append(kmsr.labels_)
centers.append(kmsr.cluster_centers_)
radii.append(kmsr.cluster_radii_)
titles.append(f"{algo}: {sum(kmsr.cluster_radii_):.3f}, Time: {end:.3f}s")
plot_multiple_results(
points,
clusters=labels,
centers=centers,
radii=radii,
title=titles,
)Install poetry
curl -sSL https://install.python-poetry.org | python3 -Install clang
sudo apt-get install clangSet clang variables
export CXX=/usr/bin/clang++
export CC=/usr/bin/clangInstall the package
poetry installIf the installation does not work and you do not see the C++ output, you can build the package to see the stack trace
poetry buildRun the tests
poetry run python -m unittest discover tests -vIf you use this code, please cite the following bachelor thesis:
N. Lenßen, "Experimentelle Analyse von Min-Sum-Radii Approximationsalgorithmen". Bachelorarbeit, Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf, 2024.
Moreover, depending on the selection of the algorithm parameter, you should also cite the following paper for algorithm='fpt-heuristic':
L. Drexler, A. Hennes, A. Lahiri, M. Schmidt, and J. Wargalla, "Approximating Fair K-Min-Sum-Radii in Euclidean Space," in Lecture notes in computer science, 2023, pp. 119–133. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-49815-2_9.
the following paper for algorithm='gonzalez':
T. F. Gonzalez, "Clustering to minimize the maximum intercluster distance," Theoretical Computer Science, vol. 38, pp. 293–306, Jan. 1985, doi: 10.1016/0304-3975(85)90224-5.
and the following paper for algorithm='kmeans':
D. Arthur and S. Vassilvitskii, "k-means++: the advantages of careful seeding," Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, pp. 1027–1035, Jan. 2007, doi: 10.5555/1283383.1283494.