A small python interface to the Bayesian Analysis Toolkit (BAT.jl) https://github.com/bat/BAT.jl
- Please check out the minimal example to get started below
- To understand how to define a prior + likelihood, please read this
- For experimental support of gradients, see this
There are two parts to an installation, one concerning the python side, and one the julia side:
-
Python:
pip install batty -
Julia:
import Pkg; Pkg.add(["PyJulia", "DensityInterface", "Distributions", "ValueShapes", "TypedTables", "ArraysOfArrays", "ChainRulesCore", "BAT"])
sampler.findmodeExample
The code below is showing a minimal example:
- using a gaussian likelihood and a uniform prior
- generating samples via Metropolis-Hastings
- plotting the resulting sampes
estimating the integral value via BridgeSampling
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
from batty import BAT_sampler, BAT, Distributions, jl
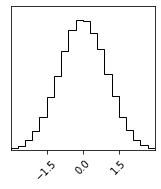
import juliacallsampler = BAT_sampler(llh=lambda x : -0.5 * x**2, prior_specs=Distributions.Uniform(-3, 3))
sampler.sample();
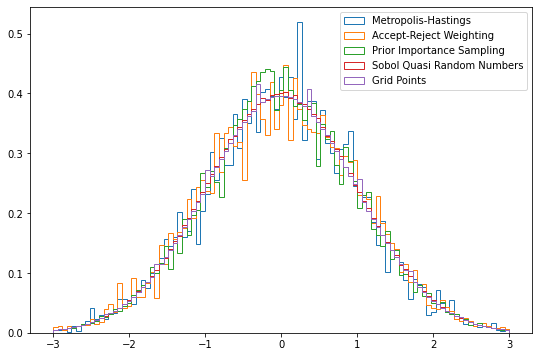
sampler.corner();There are a range of algorihtms available within BAT, and those can be further customized via arguments. Here are just a few examples:
results = {}- Metropolis-Hastings:
results['Metropolis-Hastings'] = sampler.sample(strategy=BAT.MCMCSampling(nsteps=10_000, nchains=2))- Metropolis-Hastings with Accept-Reject weighting:
results['Accept-Reject Weighting'] = sampler.sample(strategy=BAT.MCMCSampling(mcalg=BAT.MetropolisHastings(weighting=BAT.ARPWeighting()), nsteps=10_000, nchains=2))- Prior Importance Sampling:
results['Prior Importance Sampling'] = sampler.sample(strategy=BAT.PriorImportanceSampler(nsamples=10_000))- Sobol Sampler:
results['Sobol Quasi Random Numbers'] = sampler.sample(strategy=BAT.SobolSampler(nsamples=10_000))- Grid Sampler:
results['Grid Points'] = sampler.sample(strategy=BAT.GridSampler(ppa=1000))Plotting the different results:
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(9,6))
bins=np.linspace(-3, 3, 100)
for key, item in results.items():
plt.hist(item.v, weights=item.weight, bins=bins, density=True, histtype="step", label=key);
plt.legend()<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7fdfc061a220>
Priors are specified via Julia Distributions, multiple Dimensions can be defined via a dict, where the key is the dimension name and the value the distribution, or as a list in case flat vectors with paraeter names are used.
Below the example with parameter names
s = np.array([[0.25, 0.4], [0.9, 0.75]])
prior_specs = {'a' : Distributions.Uniform(-3,3), 'b' : Distributions.MvNormal(np.array([1.,1.]), jl.Array(s@s.T))}The log-likelihood (llh) can be any python callable, that returns the log-likelihood values. The first argument to the function is the object with paramneter values, here x. If the prior is simple (i.e. like in the example in the beginning, x is directly the parameter value). If the prior is specified via a dict, then x contains a field per parameter with the value.
Any additional args to the llh can be given in the sampler, such as here d for data:
def llh(x, d):
return -0.5 * ((x.b[0] - d[0])**2 + (x.b[1] - d[1])**2/4) - x.aOr alternatively without parameter names (this will result in a flat vector):
# prior_specs = [Distributions.Uniform(-3,3), Distributions.MvNormal(np.array([1.,1.]), jl.Array(s@s.T))]
# def llh(x, d):
# return -0.5 * ((x[1] - d[0])**2 + (x[2] - d[1])**2/4) - x[0]d = [-1, 1]sampler = BAT_sampler(llh=llh, prior_specs=prior_specs, llh_args=(d,))Let us generate a few samples:
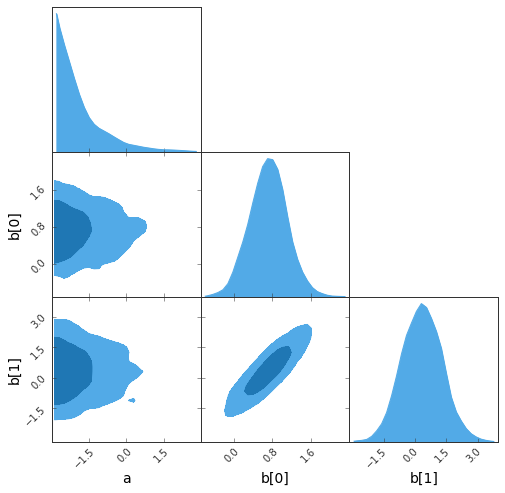
sampler.sample(strategy=BAT.MCMCSampling(nsteps=10_000, nchains=2));- The Great Triangular Confusion (GTC) plot:
sampler.gtc(figureSize=8, customLabelFont={'size':14}, customTickFont={'size':10});findfont: Font family ['Arial'] not found. Falling back to DejaVu Sans.
findfont: Font family ['Arial'] not found. Falling back to DejaVu Sans.
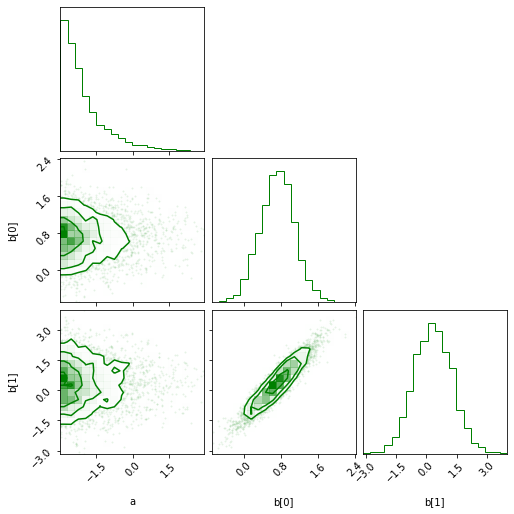
- The corner plot:
sampler.corner(color='green');First let's look at an example using flat vectors:
llh = lambda x : -0.5 * np.dot(x, x)
grad = lambda x : -x
sampler = BAT_sampler(llh=llh, prior_specs=[Distributions.Uniform(-3, 3),], grad=grad, )
# Or alternatively:
# llh_and_grad = lambda x: (-0.5 * np.dot(x, x), -x)
# sampler = BAT_sampler(llh=llh, prior_specs=[Distributions.Uniform(-3, 3),], llh_and_grad=llh_and_grad)sampler.sample(strategy=BAT.MCMCSampling(mcalg=BAT.HamiltonianMC()));
sampler.corner();sampler.findmode()(result = [0.00012339715218110216], result_trafo = [0.00012339715218110216], trafo = identity ∘ identity, trace_trafo = NamedTuple{(:v,), Tuple{Vector{Float64}}}[(v = [2.5003780712463737],), (v = [2.5003780712463737],), (v = [1.225189035623187],), (v = [-0.04999999999999982],), (v = [-0.04999999999999982],), (v = [0.02969931472644935],), (v = [0.009774486044837057],), (v = [0.004793278874433983],), (v = [-0.00018792829596908991],), (v = [-0.00018792829596908991],)], info = Results of Optimization Algorithm
* Algorithm: Nelder-Mead
* Starting Point: [2.5003780712463737]
* Maximizer: [0.00012339715218110216]
* Maximum: -1.791759e+00
* Iterations: 9
* Convergence: true
* √(Σ(yᵢ-ȳ)²)/n < 1.0e-08: true
* Reached Maximum Number of Iterations: false
* Objective Calls: 21, optargs = (algorithm = NelderMeadOpt{DoNotTransform, InitFromTarget}
trafo: DoNotTransform DoNotTransform()
init: InitFromTarget InitFromTarget()
,), kwargs = NamedTuple())
sampler.findmode(BAT.LBFGSOpt())(result = [4.654232554912596e-11], result_trafo = [1.9443995892542976e-11], trafo = DistributionTransform(BAT.StandardMvNormal{Float64}(_dim=1), ValueShapes.UnshapedNTD{NamedTupleDist{(:p0,), Tuple{Uniform{Float64}}, Tuple{ValueAccessor{ScalarShape{Real}}}, NamedTuple}}(
shaped: NamedTupleDist((p0 = Uniform{Float64}(a=-3.0, b=3.0),))
)
), trace_trafo = NamedTuple{(:v, :logd, :grad_logd), Tuple{Vector{Float64}, Float64, Vector{Float64}}}[(v = [-0.6587150350244174], logd = -2.21599390599995, grad_logd = [3.4906771750114083]), (v = [0.23765672881802102], logd = -1.105977679254204, grad_logd = [-1.5490570022891985]), (v = [0.001027968548749203], logd = -0.9189420888411827, grad_logd = [-0.006917790331040427]), (v = [1.9443995892542976e-11], logd = -0.9189385332046728, grad_logd = [-1.3085020483106803e-10])], info = Results of Optimization Algorithm
* Algorithm: L-BFGS
* Starting Point: [-0.6587150350244174]
* Maximizer: [1.9443995892542976e-11]
* Maximum: -9.189385e-01
* Iterations: 3
* Convergence: true
* |x - x'| ≤ 0.0e+00: false
|x - x'| = 1.03e-03
* |f(x) - f(x')| ≤ 0.0e+00 |f(x)|: false
|f(x) - f(x')| = 3.87e-06 |f(x)|
* |g(x)| ≤ 1.0e-08: true
|g(x)| = 1.31e-10
* Stopped by an decreasing objective: false
* Reached Maximum Number of Iterations: false
* Objective Calls: 8
* Gradient Calls: 8, optargs = (algorithm = LBFGSOpt{PriorToGaussian, InitFromTarget}
trafo: PriorToGaussian PriorToGaussian()
init: InitFromTarget InitFromTarget()
,), kwargs = NamedTuple())
Or with parameter names (here the gradient function needs to be able to return named tuples!):
from collections import namedtuple
prior = {'a':Distributions.Uniform(-3, 3), 'b': Distributions.Cauchy()}
llh = lambda x : -0.5 * x.a**2 + x.b
v = namedtuple('v', 'a b')
def grad(x):
return v(a = -x.a, b=1.)sampler = BAT_sampler(llh=llh, prior_specs=prior, grad=grad, )sampler.findmode(BAT.LBFGSOpt())(result = (a = -2.774359870100099, b = 1.3748233863972102e15), result_trafo = [-1.779160961167169, 8.292361075813613], trafo = DistributionTransform(BAT.StandardMvNormal{Float64}(_dim=2), NamedTupleDist{(:a, :b)}(…)), trace_trafo = NamedTuple{(:v, :logd, :grad_logd), Tuple{Vector{Float64}, Float64, Vector{Float64}}}[(v = [-1.2587536135732944, -1.7223257853024079], logd = -14.379301063532187, grad_logd = [3.8337762241448323, 17.76625871401564]), (v = [0.7635387123418593, 7.649261536696631], logd = 3.1433087080088902e13, grad_logd = [-3.740473440116247, 2.4394275174682822e14]), (v = [0.7635382664426248, 2.908025324267957e7], logd = 9.519928220680188e14, grad_logd = [-3.740472581583452, -2.908025324267957e7]), (v = [-2.314123355320277, 5.153011945433553e6], logd = 1.361546620342311e15, grad_logd = [2.797466899034834, -5.153011945433553e6]), (v = [0.35941433317089366, 1.2642107455691537e6], logd = 1.3740242719926018e15, grad_logd = [-2.2491330410508144, -1.2642107455691537e6]), (v = [-1.9095295505340744, 314587.89939169737], logd = 1.3747739036239808e15, grad_logd = [3.0041932888082328, -314587.89939169737]), (v = [1.0862253500010608, 78558.91268333828], logd = 1.3748203006458245e15, grad_logd = [-3.962855864264687, -78558.91268333828]), (v = [-2.8774313584103415, 19637.15728740389], logd = 1.3748231935882265e15, grad_logd = [2.991336448955899, -19637.15728740389]), (v = [0.11302692230648326, 4911.984602697699], logd = 1.374823374333412e15, grad_logd = [-0.7551326673718901, -4911.984602697699]), (v = [-0.6418462549610223, 1231.0062794741957], logd = 1.374823385639519e15, grad_logd = [3.4413763327035025, -1231.0062794741957]), (v = [2.7908181536295023, 310.85380281622554], logd = 1.374823386348885e15, grad_logd = [-2.936232052477065, -310.85380281622554]), (v = [-0.1160917967360473, 80.96146595642469], logd = 1.374823386393931e15, grad_logd = [0.7753005443326515, -80.96146595642469]), (v = [0.638783237264492, 23.19797499535367], logd = 1.3748233863969382e15, grad_logd = [-3.432151104065695, -23.19797499535367]), (v = [-2.175796434545086, 9.380111523275037], logd = 1.3748233863971578e15, grad_logd = [2.829155556024242, -9.380111523275037])], info = Results of Optimization Algorithm
* Algorithm: L-BFGS
* Starting Point: [-1.2587536135732944,-1.7223257853024079]
* Maximizer: [-1.779160961167169,8.292361075813613]
* Maximum: 1.374823e+15
* Iterations: 14
* Convergence: false
* |x - x'| ≤ 0.0e+00: false
|x - x'| = 1.09e+00
* |f(x) - f(x')| ≤ 0.0e+00 |f(x)|: false
|f(x) - f(x')| = 8.00e-15 |f(x)|
* |g(x)| ≤ 1.0e-08: false
|g(x)| = 8.29e+00
* Stopped by an decreasing objective: false
* Reached Maximum Number of Iterations: false
* Objective Calls: 204
* Gradient Calls: 204, optargs = (algorithm = LBFGSOpt{PriorToGaussian, InitFromTarget}
trafo: PriorToGaussian PriorToGaussian()
init: InitFromTarget InitFromTarget()
,), kwargs = NamedTuple())
Or a simple llh with no vector nor tuple:
llh = lambda x : -0.5 * np.dot(x, x)
grad = lambda x : -x
sampler = BAT_sampler(llh=llh, prior_specs=Distributions.Uniform(-3, 3), grad=grad, )sampler.findmode(BAT.LBFGSOpt())(result = -4.440892098500626e-16, result_trafo = [-9.599424391232986e-17], trafo = Base.Fix2{typeof(unshaped), ScalarShape{Real}}(ValueShapes.unshaped, ScalarShape{Real}()) ∘ DistributionTransform(BAT.StandardUvNormal{Float64}(), Uniform{Float64}(a=-3.0, b=3.0)), trace_trafo = NamedTuple{(:v, :logd, :grad_logd), Tuple{Vector{Float64}, Float64, Vector{Float64}}}[(v = [0.19839644385007574], logd = -1.0499145108671066, grad_logd = [-1.3057027231751668]), (v = [-0.1257368729646586], logd = -0.9718972381306173, grad_logd = [0.8386048377455525]), (v = [-9.167475784471746e-6], logd = -0.9189385334874584, grad_logd = [6.169324290536366e-5]), (v = [-9.599424391232986e-17], logd = -0.9189385332046728, grad_logd = [1.1589900163878561e-15])], info = Results of Optimization Algorithm
* Algorithm: L-BFGS
* Starting Point: [0.19839644385007574]
* Maximizer: [-9.599424391232986e-17]
* Maximum: -9.189385e-01
* Iterations: 3
* Convergence: true
* |x - x'| ≤ 0.0e+00: false
|x - x'| = 9.17e-06
* |f(x) - f(x')| ≤ 0.0e+00 |f(x)|: false
|f(x) - f(x')| = 3.08e-10 |f(x)|
* |g(x)| ≤ 1.0e-08: true
|g(x)| = 1.16e-15
* Stopped by an decreasing objective: false
* Reached Maximum Number of Iterations: false
* Objective Calls: 7
* Gradient Calls: 7, optargs = (algorithm = LBFGSOpt{PriorToGaussian, InitFromTarget}
trafo: PriorToGaussian PriorToGaussian()
init: InitFromTarget InitFromTarget()
,), kwargs = NamedTuple())