This is a Haskell binding to the wiringPi library, which allows you to interface with the GPIO pins on the Raspberry Pi. Unlike some other solutions for using the Raspberry Pi's GPIO pins, wiringPi provides access to more advanced features, such as enabling the internal pull-up or pull-down resistors.
To use this library, you must either run as root, or set the
WIRINGPI_GPIOMEM environment variable. (Set it to anything; the
value does not matter.) However, PWM will not work if
WIRINGPI_GPIOMEM is set.
This library will only build on the Raspberry Pi. Before building this library, you must install the "wiringPi" C library on your Raspberry Pi, like this:
sudo apt-get install wiringpi
Tested on a Raspberry Pi Model B, with Raspbian Jessie Lite, using the system-provided Haskell compiler. (GHC 7.6.3.)
WiringPi allows each pin to be identified by one of three names. A
pin can be identified by its physical pin number, by its Broadcom GPIO
number (this is the one most commonly used in the Raspberry Pi
community), or by its wiringPi pin number. The Pin type has three
constructors (Wpi, Gpio, and Phys), allowing you to call a pin
by any of its three names. These names are synonymous and
interchangeable.
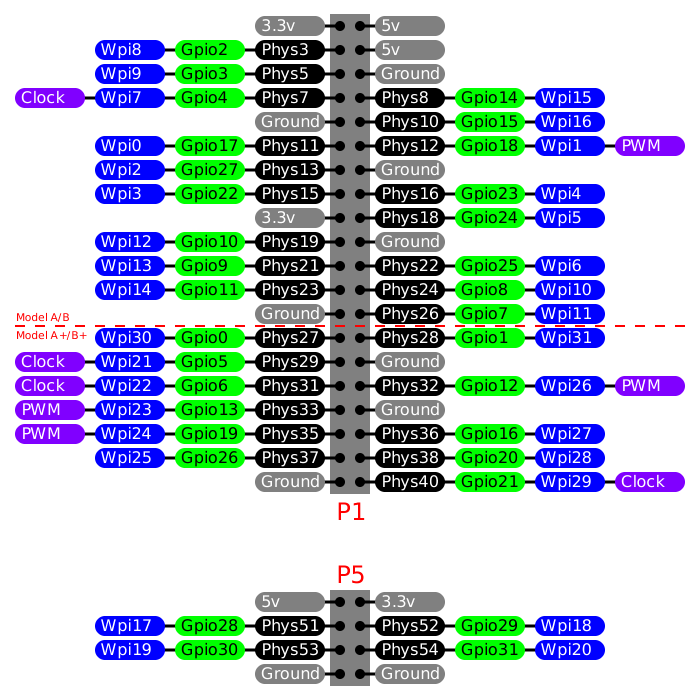
The following diagram illustrates the three names of each pin, and
also identifies which pins can be placed in PWM_OUTPUT mode or
GPIO_CLOCK mode.
Similar diagrams are available on the wiringPi site or on pinout.xyz.
One additional wrinkle is that some very early Raspberry Pis use
different Broadcom GPIO numbers for a few of the pins. WiringPi
automatically takes this into account, but it means that equality for
Pin actually depends on which board revision you have.
This Haskell binding is licensed under the 3-clause BSD license, and
the examples in the examples directory are in the public domain.
However, be aware that the wiringPi C library itself is licensed under
the LGPLv3+.
There are several examples in the examples directory. You can run
each example by wiring up a circuit on a breadboard as specified by
the comments in the example. Or, for something more permanent and
professional-looking, you can use the
hs-wiringPi test board.
The hs-wiringPi test board can be used with all of the examples,
except for wpi-fishdish, which requires the
Fish Dish
board instead.