PadoGrid | Catalogs | Manual | FAQ | Releases | Templates | Pods | Kubernetes | Docker | Apps | Quick Start
PadoGrid | Catalogs | Manual | FAQ | Releases | Templates | Pods | Kubernetes | Docker | Apps | Quick Start
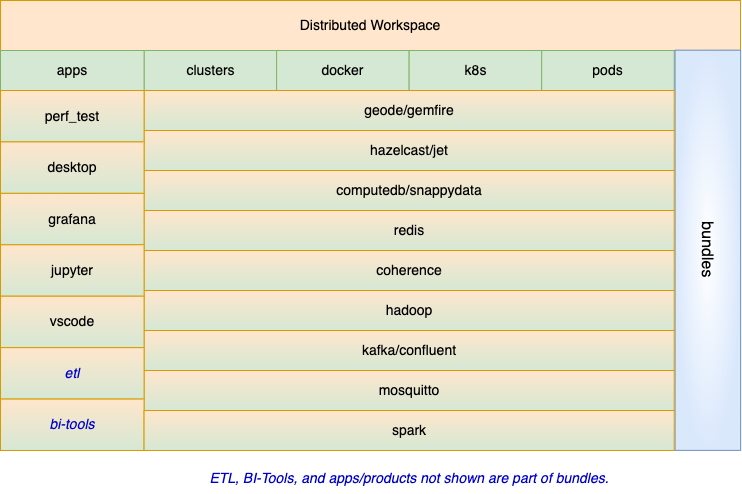
PadoGrid provides a distributed workspace environment for easily deploying and managing out-of-the-box turnkey solutions to cluster architecture use cases. The solutions come in the form of bundles which you simply install and run. See the following links for details.
- May 24, 2024 - PadoGrid v1.0.0 released! This is the first major release that officially supports product upgrade and maintenance. Look for
compliant bundles in the bundle catalogs.
-
Need Hazelcast Managment Center dashboards in Granana? Check out PadoGrid Hazelcast Dashboards (PHD).
-
Did you know PadoGrid can quickly spawn multiple clusters of different products on your laptop without resorting to containers? Check out Non-Conflicting Clusters Example.
You can install PadoGrid and the supported data grid products by running the interactive install_padogrid script. Copy and paste the following commands into your terminal.
curl -O -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/padogrid/padogrid/develop/padogrid-deployment/src/main/resources/common/bin_sh/install_padogrid
chmod 755 install_padogrid
./install_padogrid✏️ Note that install_padogrid is part of PadoGrid. Once PadoGrid is installed, you can run install_padogrid at any time to upgrade or downgrade products.
Quick Start provides detailed instructions.
✏️ The latest PadoGrid snapshot release is available if you cannot wait till the next release. It is automatically built when there were changes made in RELEASE_NOTES.md. You can download it from Releases or using install_padogrid.
To run PadoGrid as a container, please follow the instructions in the links below.
PadoGrid binary downloads are available from the Releases page. If your host does not have access to the Internet and you are unable to run install_padogrid then you can download a version from this link and install it manually.
Download links to all the supported data grids are also provided in the following page:
Online use case bundles:
PadoGrid is a collection of add-on components and tools specifically designed for data grid products to deliver out-of-the-box, shrink-wrapped solutions. It introduces the concept of distributed workspaces for creating DevOps environments in which use cases can be quickly developed, tested, deployed and shared.
A workspace provides a sandbox environment completely isolated from other workspaces and can host a wide range of software components from a simple app to a highly complex ecosystem with many data grid clusters, apps, VMs, and Docker/Kubernetes containers. You can, for example, create a workspace that federates multiple data grid clusters serving inventory and sales data, a workspace that streams database CDC records via Kafka, a workspace that handles streamed data into the federated clusters via one or more Apache Spark or Hazelcast Jet clusters, and yet another workspace that integrates data analytics tools for performing AI/ML operations and creating reports. PadoGrid consolidates your workspaces into a single operations center.
A workspace snapshot can be taken at any time in the form of a bundle that can be quickly deployed and run on another workspace created by another user on another platform. Because of their portability, bundles provide the means to shrink-wrap fully operational use cases. PadoGrid includes bundle catalogs from which you can search your use cases.
- Distributed Workspaces
- Multiple Data Grid Products
- Performance Test App
- Data Grid Desktop App
- Grafana App
- Kubernetes Autoscaler
- Docker Clusters
- PadoGrid (Vagrant) Pods
- Hazelcast Query Language (HQL)
- MQTT Virtual Clusters
- Integrated Tools (JupyterLab/VS Code)
- Use Cases via Online Bundles
- Maven 3.x
- JDK 1.8+
There are a number of ways to build a PadoGrid distribution. For building a standard distribution release, run the build_dist.sh script as follows.
# Include all products and their man pages (standard distribution)
./build_dist.sh -allYou can also build distributions that are tailored to your needs as described in the following link.
Released versions of PadoGrid are normally installed by running the install_padogrid command. For those that you have built, however, must be installed manually as describe in this section.
Upon successful build, the following distribution files will be generated.
padogrid-deployment/target/assembly/padogrid_<version>.tar.gz
padogrid-deployment/target/assembly/padogrid_<version>.zipInflate one of the distribution files in your file system. For example,
mkdir -p ~/Padogrid/products
tar -C ~/Padogrid/products/ -xzf padogrid_0.9.34-SNAPSHOT.tar.gz
cd ~/Padogrid/products
tree -L 1 padogrid_0.9.34-SNAPSHOTOutput:
padogrid_0.9.34-SNAPSHOT
├── LICENSE
├── NOTICE
├── README.md
├── RELEASE_NOTES.md
├── apps
├── bin_sh
├── coherence
├── etc
├── geode
├── hadoop
├── hazelcast
├── kafka
├── lib
├── mosquitto
├── none
├── pods
├── redis
├── snappydata
├── spark
└── workspace✏️ If you have run install_padogrid, then you have already initialized PadoGrid and you can skip this section.
To use PadoGrid, you must first create an RWE (Root Workspace Environment) by running the interactive command, create_rwe, to specify the workspaces directory and the product installation paths.
~/Padogrid/products/padogrid_0.9.34-SNAPSHOT/bin_sh/create_rweTo save your workspaces created in the container, it is recommended that you mount a data volume along with ports exposed as follows.
# Docker
docker run --name padogrid -h padogrid -d \
--mount type=volume,source=padogrid,target=/opt/padogrid \
-p 8888:8888 -p 1883:1883 -p 1884:1883 -p 1885:1883 \
-p 8080:8080 -p 5701:5701 -p 5702:5702 -p 5703:5703 \
-p 9401:9401 -p 9402:9402 -p 9403:9403 \
-p 3000:3000 -p 9090:9090 -p 5006:5006 \
-e PADOGRID_HTTPS_ENABLED=true padogrid/padogrid
# Podman
podman run --name padogrid -h padogrid -d \
--mount type=volume,source=padogrid,target=/opt/padogrid \
-p 8888:8888 -p 1883:1883 -p 1884:1883 -p 1885:1883 \
-p 8080:8080 -p 5701:5701 -p 5702:5702 -p 5703:5703 \
-p 9401:9401 -p 9402:9402 -p 9403:9403 \
-p 3000:3000 -p 9090:9090 -p 5006:5006 \
-e PADOGRID_HTTPS_ENABLED=true padogrid/padogridOnce the PadoGrid container is started, you can access the container as follows.
- PadoGrid URL: https://0.0.0.0:8888
- Password:
padogrid
# Docker
docker exec -it padogrid /bin/bash
# Podman
poman exec -it padogrid /bin/bash✏️ PadoGrid Docker containers follow the same version conventions as the build except for the SNAPSHOT versions which also include a build number starting from 1. For example, the padogrid/paadogrid:0.9.34-SNAPSHOT-2 image has the build number 2. The SNAPSHOT versions are for testing only and subject to removal without notice.
For additional details, see the Docker section of the manual.
You can run PadoGrid on Kubernetes as shown below. The PadoGrid container stores workspaces in the /opt/padogrid/workspaces directory, which you can mount to a persistent volume as needed.
# kubectl
kubectl run padogrid --image=docker.io/padogrid/padogrid
# oc
oc run padogrid --image=docker.io/padogrid/padogridTo login to the PadoGrid pod, make sure to specify the command, bash, as follows.
# kubectl
kubectl exec -it padogrid -- bash
# oc
oc exec -it padogrid -- bashIf you have a Hazelcast cluster running in the same namespace (project) as PadoGrid, then you can run the perf_test app immediately without any manking changes.
If they are running in different namespaces, then set the PadoGrid container environment variables as follows before running the the perf_test app.
export NAMESPACE=<Kubernetes namespace/project>
export HAZELCAST_SERVICE=<Hazelcast Kubernetes service>
# Default cluster name is "dev".
export HAZELCAST_CLUSTER_NAME=<cluster name>
create_app
cd_app perf_test; cd bin_sh
./test_ingestion -runTo delete the PadoGrid pod:
# kubectl
kubectl delete pod paodgrid
# oc
oc delete pod padogridYou may encounter a random userid assigned by Kubernetes and OpenShift instead of the required fixed userid, padogrid, especially when you deploy the PadoGrid container. The following link provides further details on running PadoGrid with the fixed userid when deployed in OpenShift.
Deploying PadoGrid in OpenShift
PadoGrid natively supports the following data grid, messaging, and analytics products.
The PadoGrid Manual describes product concepts and provides complete instructions for configuring and operating PadoGrid. It also includes many tutorials and working examples that you can quickly try out on your laptop.
PadoGrid has been built with use cases in mind. It aims to deliver out-of-the-box turnkey solutions on top of data grid products. The bundle catalogs provide compiled lists of readily available solutions. Just install and run.
You can also create online bundles hosted by your repos. The following link provides how-to instructions.
Creating your own online bundles is made easy by using the bundle templates. The following link povides template links.
The FAQ link aims to provide a comprensive collection of PadoGrid Q&As including a series of topics on how to build distributed systems using PadoGrid.
 PadoGrid | Catalogs | Manual | FAQ | Releases | Templates | Pods | Kubernetes | Docker | Apps | Quick Start
PadoGrid | Catalogs | Manual | FAQ | Releases | Templates | Pods | Kubernetes | Docker | Apps | Quick Start