Table of Contents
Many thanks to Tobias Zaenker, Rohit Menon, and Prof. Dr. Maren Bennewitz for the research opportunity. If using capsicum_superellipsoid_detector for scientific publications, please cite our paper, available here (Arxiv) and here (IEEE), using this bibtex or plain citation:
S. Marangoz, T. Zaenker, R. Menon and M. Bennewitz, "Fruit Mapping with Shape Completion for Autonomous Crop Monitoring," 2022 IEEE 18th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), 2022, pp. 471-476, doi: 10.1109/CASE49997.2022.9926466.
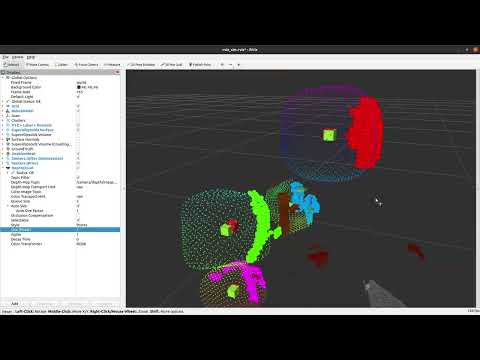
Autonomous crop monitoring is a difficult task due to the complex structure of plants. Occlusions from leaves can make it impossible to obtain complete views about all fruits of plants (e.g. Capsicum). Therefore, accurately estimating the shape and volume of fruits from partial information is crucial to enable further advanced automation tasks such as yield estimation and automated fruit picking. In this work, we present an approach for faster and better estimating shapes of fruits by fitting superellipsoids. The ROS node applies;
- Euclidean Clustering to the input point cloud for fruit separation,
- Computes surface normals then estimates fruit centers with the least-squares intersection of lines approach,
- Matches superellipsoids to the clustered points with a non-linear least-squares approach. Also, some priors are used (estimated center, superellipsoid scaling constraints),
- Predicts missing surfaces on a fruit. This step is done by uniform-like sampling of the superellipsoid surface and then only selecting sampled points having the closest distance to data points higher than the threshold.
Youtube video link for the demo of this project:
Meeting notes (for HiWi) can be found here.
Some prototypes and experiments (implemented in Python) can be found below. Selected ideas are already implemented in C++:
| Related File | Description |
|---|---|
| detector_prototype.py | First prototype Python code with ROS1 support. New ideas are not implemented here. |
| simulate_depth_noise.py | A simple code for adding noises (gaussian noise, shadowing effect, salt and pepper, waves) to the pointcloud data obtained from Gazebo simulator. Note: Currently using simulate_depth_noise.cpp instead. |
| optimization.ipynb | Least-Squares optimization for fitting superellipsoid to partial pointcloud. |
| intersection_of_lines.ipynb | Least-Squares estimation of capsicum centroid using surface normals. |
| cost_functions.ipynb | Analyzing of different cost functions. |
| find_missing_part_of_spherical_data.ipynb | Experiments for finding missing parts of spherical data. Can be extended to superellipsoidical data. (Note: Embedded videos may not be properly visualized on Github. I recommend this Chrome extension for opening the notebook.) |
| superellipsoid_fibonacci_projection_sampling.ipynb | Uniform-like sampling of superellipsoid surface points. See my blog post for more. |
Packages needed for running launch files. Try running start_bag.launch if you don't want to install these packages.
- voxblox (3D mapping)
$ cd ~/catkin_ws/src
$ mkdir voxblox
$ cd voxblox
$ git clone git@github.com:ethz-asl/voxblox.git
$ wstool init . ./voxblox/voxblox_ssh.rosinstall
- ur_with_cam_gazebo (simulator)
- roi_viewpoint_planner (robotic arm planner)
- pointcloud_roi (alternative for agrobot_mrcnn_ros on simulation environment for mask extraction)
- agrobot_mrcnn_ros (deep learning model for detecting sweet peppers in camera images)
Dependencies needed only for compiling and running the node (excluding launch files).
-
Ubuntu 20.04 + ROS Noetic
-
- Only used for publishing
~superellipsoids_volume_octomap. - Also, octomap_vpp_rviz_plugin may be useful for visualization.
- Only used for publishing
-
Ceres Solver: (I have developed the project using the version 2.x.x but both versions should be OK.)
- Apt Installation (version 1.x.x)
$ sudo apt install libceres-dev
- Manual Installation (version 2.x.x)
$ sudo apt-get install cmake libgoogle-glog-dev libgflags-dev libatlas-base-dev libeigen3-dev libsuitesparse-dev $ cd ~/catkin_ws # or another path... don't delete the folder afterwards to be able to uninstall it $ git clone https://github.com/ceres-solver/ceres-solver.git $ cd ceres-solver $ mkdir build $ cd build $ cmake .. -DBUILD_TESTING=OFF -DBUILD_EXAMPLES=OFF -DBUILD_BENCHMARKS=OFF -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON $ make -j8 $ sudo make install # run "sudo make uninstall" for uninstalling if needed
-
Others: Octomap, PCL, etc. Defined in
package.xml.
$ cd catkin_ws/
$ rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r # install missing dependencis$ cd catkin_ws/
$ catkin build --cmake-args -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=ReleaseFor running the node use the following command:
$ $ roslaunch capsicum_superellipsoid_detector start_bag.launch # for a quick demo
# OR
$ roslaunch capsicum_superellipsoid_detector start_sim.launch # for simulation
# OR
$ roslaunch capsicum_superellipsoid_detector start_real.launch # for real world-
p_cost_type: 2Optimization cost function for matching superellipsoids to the input points.
Note:
RADIAL_EUCLIDIAN_DISTANCEandSOLINAworks pretty well. Others have several problems.CostFunctionType::NAIVE = 0
CostFunctionType::LEHNERT = 1
CostFunctionType::RADIAL_EUCLIDIAN_DISTANCE = 2
CostFunctionType::SOLINA = 3
CostFunctionType::SOLINA_DISTANCE = 4
-
p_prior_center: 0.1- Alpha value for the prior which enforces optimized center t and center estimated via surface normals p to be close to each other. Higher values increases the regularization.
-
p_prior_scaling: 0.1- Beta value for the prior which enforces a, b, c values which defines scaling of superellipsoid to be close to each other. Higher values increases the regularization.
-
p_missing_surfaces_num_samples: 300- Number of points for sampling with projected fibonacci sphere method for missing surface points prediction.
-
p_missing_surfaces_threshold: 0.015- In meters. Points sampled with projected fibonacci sphere method are compared to the input data points. If the distance is higher than the threshold sampled point is marked as a missing surface point.
-
p_min_cluster_size: 100- Discards clusters smaller than p_min_cluster_size.
-
p_max_cluster_size: 10000- Discards clusters larger than p_max_cluster_size.
-
p_max_num_iterations: 100- Maximum number of non-linear least-squares optimization.
-
p_cluster_tolerance: 0.01- In meters. sGroups two points having smaller distance than p_cluster_tolerance into the same cluster.
-
p_estimate_normals_search_radius: 0.015- In meters. Uses points closer than p_estimate_normals_search_radius for normal vector computation.
-
p_estimate_cluster_center_regularization: 2.5- Regularization for intersection of lines computation. Defines bias towards mean of cluster points. Higher values brings the result towards the bias point. Useful when there are not enough surfaces.
-
p_pointcloud_volume_resolution: 0.001- In meters. Resolution of ~superellipsoids_volume message.
-
p_octree_volume_resolution: 0.001- In meters. Resolution of ~superellipsoids_volume_octomap message.
-
p_print_ceres_summary: false- Prints cost, gradients, extra information, etc. for each optimization step.
-
p_use_fibonacci_sphere_projection_sampling: false- This only affects the the output of ~superellipsoids_surface message. I personaly find surface sampled with parametric representation easier to perceive.
- If true, uses our approach for uniform-like sampling of superellipsoid .
- If false, uses parametric representation which is not uniform-like.
- See superellipsoid_fibonacci_projection_sampling.ipynb for the comparsion.
-
p_world_frame: "world"- World transform frame.
~pc_in ("sensor_msgs/PointCloud2")
- RGBXYZ pointcloud as the input (e.g. voxblox output can be used as the input). Currently RGB information is not used. Some modifications may be needed to feed XYZ only pointcloud.
~superellipsoids("superellipsoid_msgs/SuperellipsoidArray")- Optimized superellipsoids output. Headers are the same for all superellipsoids.
~clusters("sensor_msgs/PointCloud2")- RGBXYZ pointcloud with each cluster has a different RGB color. Colors may be changed between messages for the same clusters. Recommended only for debugging.
~superellipsoids_surface("sensor_msgs/PointCloud2")- XYZ pointcloud for the surface of superellipsoids.
~centers_prior("sensor_msgs/PointCloud2")- XYZ pointcloud for predicted centers via only using surface normals. Recommended only for debugging.
~centers_optimized("sensor_msgs/PointCloud2")- XYZ pointcloud for centers computed after the superellipsoid optimization. Centers for failed optimizations will not be published. Recommended only for debugging.
~superellipsoids_volume("sensor_msgs/PointCloud2")- XYZ pointcloud for the volume of superellipsoids. The volume is sampled uniform with a fixed resolution and then all points are transformed to the real position.
~superellipsoids_volume_octomap("octomap_msgs::Octomap")- XYZ octomap_vpp::CountingOcTree for the volume of superellipsoids. The volume is sampled uniform with a fixed resolution and then all points are transformed to the real position. The count value represents cluster index of the superellipsoid.
~surface_normals_marker("visualization_msgs::MarkerArray")- Arrow markers for visualizing surface normals. Surface normals are computed w.r.t. predicted cluster center. Only recommended for debugging. Use
~xyz_label_normalfor further processing.
- Arrow markers for visualizing surface normals. Surface normals are computed w.r.t. predicted cluster center. Only recommended for debugging. Use
~xyz_label_normal("sensor_msgs/PointCloud2")- XYZLNormal pointcloud for all clustered points. Labels are indicating cluster indexes and normals are computed w.r.t. predicted cluster center.
~missing_surfaces("sensor_msgs/PointCloud2")- XYZLNormal pointcloud representing (estimated) missing data points on an superellipsoid. Labels are indicating cluster indexes and normals are directed towards the optimized center.
world-> Input Pointcloud Frame
There are no services for the written node. But voxblox needs a std_srvs/Empty for publishing pointclouds of mapped plants which will be also triggering the computation of the superellipsoid detector node. Currently this task is assigned to scripts/trigger_voxblox.py which calls the related service in a fixed interval.
- Accessing to voxblox mesh (vertices and normas) directly would be better. This can take away the need to estimate normals. But this needs some workarounds and code modifications in voxblox.
- Better clustering / instance segmentation.
- 3D mapping with Instance segmentation. Mapping with masking pointcloud impacts the quality.
- Use of surface normals instead of a single estimated center in the optimization process. This may work better for non-sphere like capsicums.
- Sometimes capsicums may have weird shapes (not like a sphere nor superellipsoid, not symmetrical, etc.). Combination of multiple superellipsoids for modeling the fruit surface would be better. On the other hand, estimating the missing parts of the shape becomes difficult this way.
- Loss functions can be used against outliers: http://ceres-solver.org/nnls_modeling.html#lossfunction