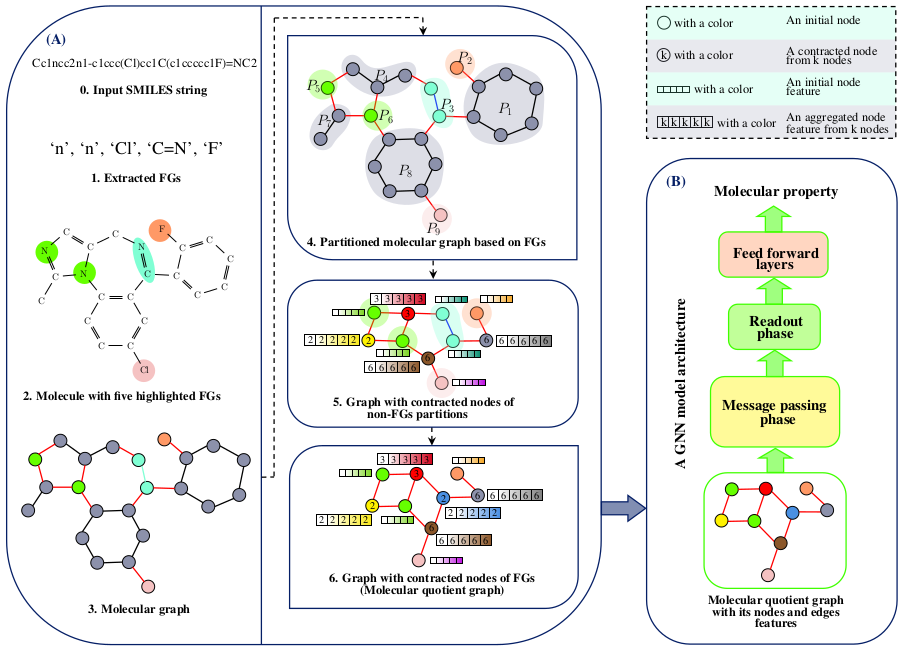
FunQG is a novel graph coarsening framework specific to molecular data, utilizing Functional groups based on a graph-theoretic concept called Quotient Graph. FunQG can accurately complete various molecular property prediction tasks with a significant parameters reduction.
The overview of FunQG framework. The left figure (A) illustrates the application of the FunQG framework to a molecule to find its corresponding coarsened graph, named molecular quotient graph. The right figure (B) shows the application of a GNN architecture to the graph obtained from the FunQG to predict the property of the molecule. In the molecular graph, a specific color corresponds to each FG (its edges and nodes). Also, edges that have exactly one common node with an FG are drawn in red. The remained edges are drawn in black.The resulting graphs of the FunQG are much smaller than the molecular graphs. Therefore, a GNN model architecture requires much less depth in working with resulting graphs compared to working with molecular graphs. Thus, using FunQG reduces the computational costs compared to working with molecular graphs. We utilize one Intel (R) Xeon (R) E5-2699 v4 @ 2.20GHz CPU for training, testing, and hyperparameter tuning of a GNN model on each dataset in a relatively short time. Therefore, training the models is very fast and is possible on a standard laptop with only one CPU.
PyTorch >= 1.9.0
DGL >= 0.6.0
Ray Tune >= 1.9.0 (for hyperparameters optimization)
git clone https://github.com/hhaji/funqg.git
cd ./funqgpython graph_generator.py --gen_names_data <list_of_datasets> --splits '["scaffold"]'usage: graph_generator.py [-h]
--name_graph Name of the constructed graph ("funqg" means FunQG graph and "mg" means molecular graph)
--current_dir Current directory containing codes and data folder
--gen_names_data <Required> A string containing a list of data names to generate graph data, e.g. '["tox21", "bbbp"]'
--splits A string containing a list of split types to generate graph data, e.g. '["scaffold"]'
--generation_seeds A string containing a list of random seeds to generate graph data, e.g. '[0, 1, 2]'
--HQ_first_aggregation_op mean, sumpython train_eval_run.py --name_data <dataset> --current_dir <path> --config <config>usage: train_eval_run.py [-h]
--name_graph Name of the constructed graph ("funqg" means FunQG graph and "mg" means molecular graph)
--name_data tox21, toxcast, clintox, sider, bbbp, bace, freesolv, esol, lipo, muv, hiv, qm7, qm8, pdbbind_r, pdbbind_c, pdbbind_f
--current_dir Current directory containing codes and data folder
--atom_messages Whether to use atoms (MPNN) or edges (DMPNN) for message passing
--global_feature Whether to use global features
--max_norm_status Whether to use max-norm regularization
--scaler_regression Whether to use Standard scaler for regression tasks
--division scaffold, random
--batch_size Batch size
--evaluate_saved Whether just to compute test scores for the best-saved models or train models first
--n_splits Number of splits for CV
--num_epochs Number of epochs
--device cpu, cuda
--patience Number of patience of early stopping
--config A configuration of hyperparameters as an string, e.g.,
{"GNN_Layers": 5.0, "dropout": 0.15, "lr": 0.0005}'python hyper_tuning_run.py --name_data <dataset> --current_dir <path>usage: hyper_tuning_run.py [-h]
--name_graph Name of the constructed graph ("funqg" means FunQG graph and "mg" means molecular graph)
--name_data tox21, toxcast, clintox, sider, bbbp, bace, freesolv, esol, lipo, muv, hiv, qm7, qm8, pdbbind_r, pdbbind_c, pdbbind_f
--current_dir Current directory containing codes and data folder
--atom_messages Whether to use atoms (MPNN) or edges (DMPNN) for message passing
--global_feature Whether to use global features
--max_norm_status Whether to use max-norm regularization
--scaler_regression Whether to use Standard scaler for regression tasks
--division scaffold, random
--batch_size Batch size
--name_scheduler None, asha, bohb, median
--name_search_alg None, optuna, bohb, hyperopt
--num_samples Number of times to sample from the hyperparameter space
--training_iteration Number of iteration of training for hyperparameter tuning
--max_concurrent Maximum number of trials to run concurrently
--num_cpus Number of CPUs (CPU_core*Thread_per_core) for hyperparameter tuning
--num_gpus Number of GPUs for hyperparameter tuning
--n_splits Number of splits for CV- Yavar Taheri Yeganeh - YavarYeganeh
- Ali Hojatnia - alihojatnia
Hajiabolhassan, H., Taheri, Z., Hojatnia, A., & Yeganeh, Y. T. (2022). FunQG: Molecular Representation Learning Via Quotient Graphs. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2207.08597